VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid (informally known as TKG) (multi-cloud) provides organizations with a consistent, upstream-compatible, regional Kubernetes substrate that is ready for end-user workloads and ecosystem integrations. It delivers an open source aligned Kubernetes distribution with consistent operations and management to support infrastructure and app modernization.
An air-gapped installation method is used when the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid components (bootstrapper and cluster nodes) are unable to connect to the Internet to download the installation binaries from the public VMware Registry during Tanzu Kubernetes Grid installation or upgrade.
The scope of the document is limited to providing deployment steps based on the reference design in Tanzu Kubernetes Grid on NSX-T Networking and it does not cover deployment procedures for the underlying SDDC components.
Supported Component Matrix
The following table provides the component versions and interoperability matrix supported with the reference design:
| Software Components | Version |
|---|---|
| Tanzu Kubernetes Grid | 2.3.0 |
| VMware vSphere ESXi | 8.0 U1 or later |
| VMware vCenter (VCSA) | 8.0 U1 or later |
| NSX Advanced Load Balancer | 22.1.3 |
| VMware NSX | 4.1.0.2 |
For the latest information about software versions that can be used together, see the Interoperability Matrix.
Prepare the Environment for Deployment of Tanzu Kubernetes Grid
Before deploying Tanzu Kubernetes Grid in the your VMware NSX environment, ensure that your environment is set up as described in the following sections:
General Requirements
- A vCenter with NSX backed environment.
-
Ensure that the following NSX configurations are complete:
The following configurations provide only a high-level overview of the required NSX configuration. For more information, see NSX Data Center Installation Guide and NSX Data Center Product Documentation.
- NSX manager instance is deployed and configured with Advanced or higher license.
- vCenter Server that is associated with the NSX Data Center is configured as Compute Manager.
- Required overlay and vLAN Transport Zones are created.
- IP pools for host and edge tunnel endpoints (TEP) are created.
- Host and edge uplink profiles are in place.
- Transport node profiles are created. This is not required if you are configuring the NSX data center on each host instead of the cluster.
- NSX data center configured on all hosts part of the vSphere cluster or clusters.
- Edge transport nodes and at least one edge cluster is created.
- Tier-0 uplink segments and tier-0 gateway is created.
- Tier-0 router is peered with uplink L3 switch.
- DHCP profile is created in NSX.
- SDDC environment has the following objects are available:
- A vSphere cluster with at least three hosts on which vSphere DRS is enabled and NSX is successfully configured.
- A dedicated resource pool to deploy the following Tanzu Kubernetes management cluster, shared services cluster, and workload clusters. The number of required resource pools depends on the number of workload clusters to be deployed.
- VM folders to collect the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid VMs.
- A datastore with sufficient capacity for the control plane and worker node VM files.
- Network time protocol (NTP) service is running on all hosts and vCenter.
- A host, server, or VM based on Linux, macOS, or Windows which acts as your bootstrap machine which has docker installed. For this deployment, a virtual machine based on Photon OS will be used.
- Depending on the OS flavor of the bootstrap VM, download and configure the following packages from Broadcom Support. To configure required packages on the Cent OS machine, see Deploy and Configure Bootstrap Machine:
- Tanzu CLI 2.3.0
- Kubectl cluster CLI 1.26.5
- A vSphere account with permissions as described in Required Permissions for the vSphere Account.
- Download and import NSX Advanced Load Balancer 22.1.3 OVA to Content Library.
- Download the following OVA files from Broadcom Support and import to vCenter. Convert the imported VMs to templates:
- Photon v3 Kubernetes v1.26.5 OVA and/or
- Ubuntu 2004 Kubernetes v1.26.5 OVA
You can also download supported older versions of Kubernetes from Broadcom Support and import them to deploy workload clusters on the intended Kubernetes versions.
In Tanzu Kubernetes Grid nodes, it is recommended not to use hostnames with “.local” domain suffix. For more information, see KB article.
Resource Pools and VM Folders
The sample entries of the resource pools and folders that need to be created are as follows.
| Resource Type | Sample Resource Pool Name | Sample Folder Name |
|---|---|---|
| NSX ALB Components | tkg-vsphere-alb-components | tkg-vsphere-alb-components |
| TKG Management components | tkg-management-components | tkg-management-components |
| TKG Shared Service Components | tkg-vsphere-shared-services | tkg-vsphere-shared-services |
| TKG Workload components | tkg-vsphere-workload | tkg-vsphere-workload |
Network Requirements
Create logical segments in NSX for deploying Tanzu Kubernetes Grid components as per Network Requirements defined in the reference architecture.
Firewall Requirements
Ensure that the firewall is set up as described in Firewall Requirements.
Subnet and CIDR Examples
For this demonstration, we used the following CIDR for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid deployment. Change the values to reflect your environment:
| Network Type | Segment Name | Gateway CIDR | DHCP Pool in NSXT | NSX ALB IP Pool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSX ALB Management Network | sfo01-w01-vds01-albmanagement | 172.16.10.1/24 | N/A | 172.16.10.100 - 172.16.10.200 |
| TKG Cluster VIP Network | sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip | 172.16.80.1/24 | N/A | 172.16.80.100 - 172.16.80.200 |
| TKG Management Network | sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgmanagement | 172.16.40.1/24 | 172.16.40.100 - 172.16.40.200 | N/A |
| TKG Shared Service Network | sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgshared | 172.16.50.1/24 | 172.16.50.100 - 172.16.50.200 | N/A |
| TKG Workload Network | sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkload | 172.16.60.1/24 | 172.16.60.100- 172.16.60.200 | N/A |
| TKG Workload VIP Network | sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvip | 172.16.70.1/24 | N/A | 172.16.70.100- 172.16.70.200 |
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Deployment Workflow
Here are the high-level steps for deploying Tanzu Kubernetes Grid on NSX networking in an air-gapped environment:
- Configure T1 Gateway and Logical Segments in NSX Data Center
- Deploy and Configure NSX Advanced Load Balancer
- Configure Bastion Host
- Install Harbor Image Registry
- Configure Bootstrap Virtual machine
- Deploy Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Management Cluster
- Deploy Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Shared Service Cluster
- Deploy Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Workload Cluster
- Deploy User-Managed Packages on Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Clusters
Configure T1 Gateway and Logical Segments in NSX-T Data Center
As a prerequisite, an NSX-T backed vSphere environment must be configured with at least one tier-0 gateway. A tier-0 gateway performs the functions of a tier-0 logical router. It processes traffic between the logical and physical networks. For more information about creating and configuring a tier-0 gateway, see NSX documentation.
This procedure comprises the following tasks:
- Add two Tier-1 Gateway
- Create Overlay-Backed Segments
Add a Tier-1 Gateway
The tier-1 logical router must be connected to the tier-0 logical router to get the northbound physical router access. The following procedure provides the minimum required configuration to create a tier-1 gateway, which is adequate to successfully deploy the Tanzu for Kubernetes Operations stack. For a more advanced configuration, see the NSX documentation.
- With admin privileges, log in to NSX Manager.
- Select Networking > Tier-1 Gateways.
- Click Add Tier-1 Gateway.
- Enter a name for the gateway.
- Select a tier-0 gateway to connect to this tier-1 gateway to create a multi-tier topology.
- Select an NSX Edge cluster. This is required for this tier-1 gateway to host stateful services such as NAT, load balancer, or firewall.
- (Optional) In the Edges field, select Auto Allocated or manually set the edge nodes.
- Select a failover mode or accept the default. The default option is Non-preemptive.
- Select Enable Standby Relocation.
-
Click Route Advertisement and ensure that following routes are selected:
- All DNS Forwarder Routes
- All Connected Segments and Service Ports
- All IPSec Local Endpoints
- All LB VIP Routes
- All LB SNAT IP Routes

-
Click Save.
-
Repeat steps from 1-11 and create another Tier-1 gateway.

DHCP configuration on Tier-1 Gateway
Complete the following steps to set the DHCP configuration in the tier-1 gateway:
- With admin privileges, log in to NSX Manager.
- Select Networking > Tier-1 Gateways.
- On the tier-1 gateway that you created earlier, click the three dots and select Edit.
-
Next to DHCP Config, click Set.
-
In the Set DHCP Configuration dialog box, set Type to DHCP Server and select the DHCP profile that you created as part of the prerequisites.

-
Click Save.
Create Overlay-Backed Segments
VMware NSX provides the option to add two kinds of segments: overlay-backed segments and VLAN-backed segments. Segments are created as part of a transport zone. There are two types of transport zones: VLAN transport zones and overlay transport zones. A segment created in a VLAN transport zone is a VLAN-backed segment and a segment created in an overlay transport zone is an overlay-backed segment.
Create the overlay backed logical segments as shown in the Overlay backed segments CIDR example. All these segments will be a part of the same overlay transport zone and they must be connected to the tier-1 gateway.
NSX ALB Management Network, TKG Cluster VIP Network, TKG Management Network & TKG Shared Service Network must be connected to sfo01w01tier1 while TKG Workload Network and TKG Workload VIP Network should be connected to sfo01w01tier2.
If you want to use TKG Cluster VIP Network to be used for applications deployed in workload cluster, connect all network segments to sfo01w01tier1 tier-1 gateway.
The following procedure provides details to create one such network which is required for the Tanzu for Kubernetes Operations deployment:
-
With admin privileges, log in to NSX Manager.
-
Select Networking > Segments.
-
Click ADD SEGMENT and enter a name for the segment. For example,
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgmanagement. -
Under Connected Gateway, select the tier-1 gateway that you created earlier.
-
Under Transport Zone, select a transport zone that will be an overlay transport zone.
-
Under Subnets, enter the gateway IP address of the subnet in the CIDR format. For example,
172.16.40.1/24
The following step is required only for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management network, shared services network, and workload network.
-
Click SET DHCP CONFIG.
DHCP Type field is set to Gateway DHCP Server and DHCP Profile is set to the profile created while creating the tier-1 gateway.
- Click Settings, select Enable DHCP Config, and enter the DHCP range and DNS server information.

-
Click Options and under Select DHCP Options, select GENERIC OPTIONS.
-
Click ADD GENERIC OPTION, add NTP servers (42) and Domain Search (119).

- Click Save to create the logical segment.
Repeat steps 1-7 to create all other required overlay-backed segments. Once completed, you should see an output similar to:

Additionally, you can create the required inventory groups and firewall rules. For more information, see the NSX Data Center Product Documentation.
Deploy and Configure NSX Advanced Load Balancer
NSX Advanced Load Balancer (ALB) is an enterprise-grade integrated load balancer that provides L4- L7 load balancer support.
NSX Advanced Load Balancer is deployed in Write Access Mode in the vSphere Environment backed by NSX-T. This mode grants NSX Advanced Load Balancer controllers full write access to the vCenter or NSX which helps in automatically creating, modifying, and removing service engines (SEs) and other resources as needed to adapt to changing traffic needs.
The sample IP address and FQDN set for the NSX Advanced Load Balancer controllers are as follows:
| Controller Node | IP Address | FQDN |
|---|---|---|
| Node 1 Primary | 172.16.10.11 | sfo01albctlr01a.sfo01.rainpole.local |
| Node 2 Secondary | 172.16.10.12 | sfo01albctlr01b.sfo01.rainpole.local |
| Node 3 Secondary | 172.16.10.13 | sfo01albctlr01c.sfo01.rainpole.local |
| HA Address | 172.16.10.10 | sfo01albctlr01.sfo01.rainpole.local |
Deploy NSX Advanced Load Balancer
As a prerequisite, you must have the NSX Advanced Load Balancer 22.1.3 OVA downloaded and imported to the content library. Deploy the NSX Advanced Load Balancer under the resource pool tkg-vsphere-alb-components and place it under the folder tkg-vsphere-alb-components.
To deploy NSX Advanced Load Balancer, complete the following steps:
- Log in to vCenter and navigate to Home > Content Libraries.
- Select the content library under which the NSX-ALB OVA is placed.
- Click on OVA & OVF Templates.
- Right-click the NSX Advanced Load Balancer image and select New VM from this Template.
- On the Select name and folder page, enter a name and select a folder for the NSX Advanced Load Balancer VM as tkg-vsphere-alb-components.
- On the Select a compute resource page, select the resource pool tkg-vsphere-alb-components.
- On the Review details page, verify the template details and click Next.
- On the Select storage page, select a storage policy from the VM Storage Policy drop-down menu and choose the datastore location where you want to store the virtual machine files.
- On the Select networks page, select the network sfo01-w01-vds01-albmanagement and click Next.
- On the Customize template page, provide the NSX Advanced Load Balancer management network details such as IP address, subnet mask, and gateway, and then click Next.
- On the Ready to complete page, review the provided information and click Finish.

A new task for creating the virtual machine appears in the Recent Tasks pane. After the task is complete, the NSX Advanced Load Balancer virtual machine is created on the selected resource. Power on the virtual machine and give it a few minutes for the system to boot. Upon successful boot up, navigate to NSX Advanced Load Balancer on your browser.
While the system is booting up, a blank web page or a 503 status code might appear.
NSX Advanced Load Balancer: Initial Setup
Once NSX Advanced Load Balancer is successfully deployed and running, navigate to NSX Advanced Load Balancer on your browser using the URL https://<IP/FQDN> and configure the basic system settings:
-
Set admin password and click on Create Account.

-
On the Welcome page, under System Settings, set backup passphrase and provide DNS information, and then click Next.

-
Under Email/SMTP, provide email and SMTP information, and then click Next.

-
Under Multi-Tenant, configure settings as follows and click Save.
- IP Route Domain: Share IP route domain across tenants
- Service Engines are managed within the: Provider (Shared across tenants)
- Tenant Access to Service Engine: Read

If you did not select the Setup Cloud After option before saving, the initial configuration wizard exits. The Cloud configuration window does not automatically launch, and you are directed to a dashboard view on the controller.
NSX Advanced Load Balancer: NTP Configuration
To configure NTP, navigate to Administration > System Settings > edit the System Settings and select DNS/NTP. Add your NTP server details and then click Save.
You might also delete the default NTP servers.

NSX Advanced Load Balancer: Licensing
This document focuses on enabling NSX Advanced Load Balancer using the license model: Enterprise License (VMware NSX ALB Enterprise).
-
To configure licensing, navigate to Administration > Licensing, and click on the gear icon to change the license type to Enterprise.

-
Select Enterprise Tier radio button as the license type and click Save.

-
Once the license tier is changed, apply the NSX Advanced Load Balancer Enterprise license key. If you have a license file instead of a license key, apply the license by selecting the Upload a License File option.

NSX Advanced Load Balancer: Controller High Availability
In a production environment, it is recommended to deploy additional controller nodes and configure the controller cluster for high availability and disaster recovery. Adding 2 additional nodes to create a 3-node cluster provides node-level redundancy for the controller and also maximizes performance for CPU-intensive analytics functions.
To run a 3-node controller cluster, you deploy the first node and perform the initial configuration, and set the cluster IP address. After that, you deploy and power on two more controller VMs, but you must not run the initial configuration wizard or change the admin password for these controllers VMs. The configuration of the first controller VM is assigned to the two new controller VMs.
The first controller of the cluster receives the Leader role. The second and third controllers work as the Follower.
Complete the following steps to configure NSX Advanced Load Balancer cluster:
-
Log in to the primary NSX Advanced Load Balancer controller and navigate to Administrator > Controller > Nodes, and then click Edit.
-
Specify Name and Controller Cluster IP, and then click Save. This IP address must be from the NSX ALB management network.

-
Deploy the 2nd and 3rd NSX Advanced Load Balancer controller nodes by using steps in Deploy NSX Advanced Load Balancer.
-
Log into the primary NSX Advanced Load Balancer controller using the Controller Cluster IP/FQDN and navigate to Administrator > Controller > Nodes, and then click Edit. The Edit Controller Configuration popup appears.
-
In the Cluster Nodes field, enter the IP address for the 2nd and 3rd controller, and then click Save.

After you complete these steps, the primary NSX Advanced Load Balancer controller becomes the leader for the cluster and invites the other controllers to the cluster as members.
NSX Advanced Load Balancer then performs a warm reboot of the cluster. This process can take approximately 10-15 minutes. You will be automatically logged out of the controller node where you are currently logged in. On entering the cluster IP address in the browser, you can see details about the cluster formation task.

The configuration of the primary (leader) controller is synchronized to the new member nodes when the cluster comes online following the reboot. Once the cluster is successfully formed, you can see the following status:

In the following tasks, all NSX Advanced Load Balancer configurations are done by connecting to the NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller Cluster IP/FQDN.
NSX Advanced Load Balancer: Certificate Management
The default system-generated controller certificate generated for SSL/TSL connections will not have the required subject alternate name (SAN) entries. Complete the following steps to create a controller certificate:
-
Log in to the NSX Advanced Load Balancer controller and navigate to Templates > Security > SSL/TLS Certificates.
-
Click Create and select Controller Certificate. You can either generate a self-signed certificate, generate CSR, or import a certificate. For the purpose of this document, a self-signed certificate will be generated.
-
Provide all required details as per your infrastructure requirements and in the Subject Alternate Name (SAN) field, provide IP address and FQDN of all NSX Advanced Load Balancer controllers including NSX Advanced Load Balancer cluster IP and FQDN, and then click Save.


-
Once the certificate is created, capture the certificate contents as this is required while deploying the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster. To capture the certificate content, click on the Download icon next to the certificate, and then click Copy to clipboard under Certificate.

-
To replace the certificate, navigate to Administration > Settings > Access Settings, and click the pencil icon at the top right to edit the system access settings, and then replace the SSL/TSL certificate and click Save.

-
Log out and log in to NSX Advanced Load Balancer.
Create Credentials
NSX Advanced Load Balancer requires credentials of VMware NSX and vCenter Server to authenticate with these endpoints. These credentials need to be created before configuring NSX Cloud.
To create a new credential, navigate to Administration > User Credentials and click Create.
- Create NSX Credential: Select the Credential Type as NSX-T from the drop-down menu, and provide a name for the credential. Under the section NSX-T Credentials, specify the username and password that NSX Advanced Load Balancer will use to authenticate with VMware NSX.

- Create vCenter Credential: Select the Credential type as vCenter from the drop-down menu and provide a name for the credential. Under the section vCenter Credentials, specify the username and password that NSX Advanced Load Balancer will use to authenticate with the vCenter server.

Create NSX Cloud and Service Engine Groups
NSX Advanced Load Balancer can be deployed in multiple environments for the same system. Each environment is called a cloud. The following procedure provides steps to create a VMware NSX cloud. As per the architecture, two service engine (SE) groups will be created.
Service Engine Group 1: Service engines associated with this service engine group hosts:
- Virtual services that load balances control plane nodes of Management Cluster and Shared services cluster.
- Virtual services for all load balancer functionalities requested by Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster and Shared services cluster.
Service Engine Group 2: Service engines part of this service engine group hosts virtual services that load balances control plane nodes and virtual services for all load balancer functionalities requested by the workload clusters mapped to this SE group.
- Based on your requirements, you can create additional SE groups for the workload clusters. - Multiple workload clusters can be mapped to a single SE group. - A Tanzu Kubernetes Grid cluster can be mapped to only one SE group for application load balancer services. - Control plane VIP for the workload clusters will be placed on the respective Service Engine group assigned through AKO Deployment Config (ADC) during cluster creation.
For information about mapping a specific service engine group to Tanzu Kubernetes Grid workload cluster, see Configure NSX Advanced Load Balancer in Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Workload Cluster.
The following components are created in NSX Advanced Load Balancer.
| Object | Sample Name |
|---|---|
| NSX Cloud | sfo01w01vc01 |
| Service Engine Group 1 | sfo01m01segroup01 |
| Service Engine Group 2 | sfo01w01segroup01 |
-
Log in to NSX Advanced Load Balancer and navigate to Infrastructure > Clouds > Create > NSX-T Cloud.

-
Enter cloud name and provide a object name prefix. Click CHANGE CREDENTIALS to connect NSX Advanced Load Balancer with VMware NSX.

-
Specify NSX-T Manager Address and select the NSX-T credential that you created earlier.

-
Under the Management Network pane, select the following options:
- Transport Zone: Overlay transport zone where you connected your NSX Advanced Load Balancer management network.
- Tier-1 Router: Tier-1 gateway where Advanced Load Balancer management network is connected.
- Overlay Segment: Logical segment that you have created for Advanced Load Balancer management.
-
Under the Data Networks pane, select the following:
- Transport Zone: Overlay transport zone where you connected your Tanzu Kubernetes Grid VIP networks.
- Tier-1 Router: Tier-1 gateway sfo01w01tier1 TKG Cluster VIP network is connected.
- Overlay Segment: Logical segment that you have created for TKG Cluster VIP Network.
- Tier-1 Router: Tier-1 gateway sfo01w01tier2 where TKG Workload VIP Network is connected.
- Overlay Segment: Logical segment that you have created for TKG Workload VIP Network.

For a single VIP network architecture, do not add sfo01w01tier2 tier-1 gateway under Data Network Segments and associated Overlay Segment. TKG Workload cluster will use the TKG Cluster VIP for both control plane and data plane network.
-
Under vCenter Servers pane, click ADD.

-
Specify a name for the vCenter server and click CHANGE CREDENTIALS to connect NSX Advanced Load Balancer with the vCenter server.

-
Select the vCenter server from the drop down and select the vCenter credential which you have created earlier.

-
Select the Content Library where Service Engine templates will be stored by NSX Advanced Load Balancer.

-
Leave the IPAM/DNS profile section empty as this will be populated later, once you have created the profiles. Click SAVE to finish the NSX-T cloud configuration.

-
Ensure that status of the NSX-T cloud is Green post creation.

-
Create a service engine group for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management clusters:
- Click on the Service Engine Group tab.
- Under Select Cloud, choose the cloud created in the previous step, and click Create.
-
Enter a name for the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management service engine group and set the following parameters:
Parameter Value High availability mode Active/Active VS Placement Compact Memory per Service Engine 4 vCPU per Service Engine 2 Use the default values for the rest of the parameters.

Under Scope tab, Specify the vCenter server endpoint by clicking on the Add option.

Select the vCenter server from the dropdown, Service Engine Folder, vSphere cluster, and datastore for service engine placement, and then click Save.

-
Repeat steps 12 and 13 to create another service engine group for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid workload clusters. Once complete, there must be two service engine groups created.

Configure Network and IPAM Profile
As part of the cloud creation, NSX Advanced Load Balancer management and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid VIP networks have been configured in NSX Advanced Load Balancer. Since DHCP was not selected as the IP address management method in the cloud configuration, you have to specify pool of IP addresses that can be assigned to the service engine NICs and the virtual services that will be created in future.
To configure IP address pools for the networks, perform the following steps:
-
Navigate to Infrastructure > Cloud Resources > Networks and select the cloud that you have created earlier. Click on the Edit icon next for the network and configure as follows. Change the provided details as per your SDDC configuration.
Network Name DHCP Subnet Static IP Pool sfo01-w01-vds01-albmanagement No 172.16.10.0/24 172.16.10.100 - 172.16.10.200 sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip No 172.16.80.0/24 172.16.80.100 - 172.16.80.200 sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvip No 172.16.70.0/24 172.16.70.100 - 172.16.70.200 Once the networks are configured, the configuration must look like the following image.

For a single VIP network architecture, do not configure sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvip network. The sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip segment is used for control plane and data network of TKG workload cluster.
-
Once the networks are configured, set the default routes for the networks by navigating to Infrastructure > Cloud Resource > Routing.
- Ensure that VRF Context for
sfo01-w01-vds01-albmanagementnetwork is set toGlobal.- Ensure that VRF Context for
- Ensure that VRF Context for sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvip network is set to NSX tier-1 gatewaysfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervipnetwork is set to NSX tier-1 gatewaysfo01w01tier1.sfo01w01tier2.To set the default gateway for the
asfo01-w01-vds01-albmanagementnetwork, click ADD Static Route under the global VRF context and set the default gateway to gateway of the NSX Advanced Load Balancer management subnet.
To set the default gateway for the
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervipnetwork, click CREATE under the tier-1 gateway VRF context and set the default gateway to gateway of the VIP network subnet.
To set the default gateway for the
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvipnetwork, click Create under the tier-1 gatewaysfo01w01tier2VRF context and set the default gateway to the gateway of the VIP network subnet.The final configuration is shown below:

Create IPAM Profile in NSX Advanced Load Balancer and Attach to Cloud
At this point, all the required networks related to Tanzu functionality are configured in NSX Advanced Load Balancer. NSX Advanced Load Balancer provides IPAM service for TKG Cluster VIP, TKG Workload VIP and NSX ALB management network.
Perform the following steps to create an IPAM profile, and attach it to the NSX-T cloud created earlier:
-
Log in to NSX Advanced Load Balancer and navigate to Templates > IPAM/DNS Profiles > Create > IPAM Profile.

Specify the following details, and then click Save.
Parameter Value Name sfo01-w01-vcenter-ipam01 Type AVI Vintage IPAM Cloud for Usable Networks sfo01w01vc01 Usable Networks sfo01-w01-vds01-management
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvip
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvip
For a single VIP network architecture, do not add sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvip network segment to the IPAM profile.
-
Click Create > DNS Profile and provide the domain name.

-
Attach the IPAM and DNS profiles to the NSX-T cloud:
- Navigate to Infrastructure > Clouds.
- Edit the
sfo01w01vc01cloud. -
Under IPAM/DNS section, choose the IPAM and DNS profiles created earlier, and save the updated configuration.

-
Under the section DNS Resolvers, click ADD to add the DNS server that NSX-T cloud will use to resolve the hostname or FQDN of the components that will be created later.

Specify a name for the DNS and click ADD under Name Servers to add your infrastructure DNS servers. Optionally, you can specify the TTL for the DNS.

This completes the NSX Advanced Load Balancer configuration. The next step is to deploy and configure a bootstrap machine which will be used to deploy and manage Tanzu Kubernetes clusters.
Deploy and Configure Bastion Host
Bastion host is the physical or virtual machine where you download the required installation images or binaries for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid installation from the Internet. The downloaded items then need to be shipped to the bootstrap machine which is inside the air-gapped environment. The bastion host needs to have a browser installed to download the binaries from the Internet.
The bastion host needs to be deployed with the following hardware configuration:
- CPU: 1
- Memory: 4 GB
- Storage (HDD): 160 GB or greater.
The following instructions are for CentOS 7. If you are using any other operating system for your bastion host, change the commands accordingly.
Download Binaries Required for Configuring Bastion Host
-
Download Docker Engine and associated dependencies binaries using the steps provided below
### Create a directory for collecting docker installation binaries: mkdir docker-binaries && cd docker-binaries ### Add docker repository to the yum command: yum install yum-utils -y yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo ### Download docker and associated dependencies: yumdownloader --resolve docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-pluginThe
yumdownloadercommand downloads the following binaries.
-
Download Harbor OVA from the Broadcom Support.
-
Download the NSX Advanced Load Balancer OVA from Broadcom Support.
-
Download Tanzu CLI, Kubectl, and the Kubernetes OVA images from the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid product download page. Tanzu CLI and plug-ins need to be installed on the bastion host and the bootstrap machine.
-
Download the yq installation binary from mikefarah / yq GitHub repository.
Configure Bastion Host
-
Install Tanzu CLI.
tar -xvf tanzu-cli-linux-amd64.tar cd ./v0.90.1/ install tanzu-cli-linux_amd64 /usr/local/bin/tanzu chmod +x /usr/local/bin/tanzuRun the
tanzu versioncommand to check that the correct version of tanzu is installed and executable.# tanzu version version: v0.90.1 buildDate: 2023-06-29 sha: 8945351c -
Install the Tanzu CLI plug-ins.
tanzu plugin group search [i] Reading plugin inventory for "projects.registry.vmware.com/tanzu_cli/plugins/plugin-inventory:latest", this will take a few seconds. GROUP DESCRIPTION LATEST vmware-tkg/default Plugins for TKG v2.3.0 tanzu plugin install --group vmware-tkg/default [i] Installing plugin 'isolated-cluster:v0.30.1' with target 'global' [i] Installing plugin 'management-cluster:v0.30.1' with target 'kubernetes' [i] Installing plugin 'package:v0.30.1' with target 'kubernetes' [i] Installing plugin 'pinniped-auth:v0.30.1' with target 'global' [i] Installing plugin 'secret:v0.30.1' with target 'kubernetes' [i] Installing plugin 'telemetry:v0.30.1' with target 'kubernetes' [ok] successfully installed all plugins from group 'vmware-tkg/default:v2.3.0' #Accept EULA tanzu config eula accept [ok] Marking agreement as accepted. -
Download the Images.
Before performing this step, ensure that the disk partition where you download the images has 45 GB of available space.
tanzu isolated-cluster download-bundle --source-repo <SOURCE-REGISTRY> --tkg-version <TKG-VERSION> --ca-certificate <SECURITY-CERTIFICATE>- SOURCE-REGISTRY is the IP address or the hostname of the registry where the images are stored.
- TKG-VERSION is the version of Tanzu Kubernetes Grid that you want to deploy in the proxied or the air-gapped environment.
- SECURITY-CERTIFICATE is the security certificate of the registry where the images are stored. To bypass the security certificate validation, use –insecure, instead of –ca-certificate. Both the strings are optional. If you do not specify any value, the system validates the default server security certificate.
tanzu isolated-cluster download-bundle --source-repo projects.registry.vmware.com/tkg --tkg-version v2.3.0The image bundle in the form of TAR files, along with the publish-images-fromtar.yaml file, is downloaded. The YAML file defines the mapping between the images and the TAR files.
-
Download the Tanzu CLI plug-ins.
Download the plugin-inventory image along with all selected plug-in images as a tar.gz file on the local disk of a machine which has internet access using the tanzu plugin download-bundle command.
tanzu plugin download-bundle --group vmware-tkg/default:v2.3.0 --to-tar plugin_bundle_tkg_latest.tar.gz -
Copy the Files to the bootstrap Machine after bootstrap Machine deployment.
Copy the following files to the offline machine, which is the bootstrap machine in the proxied or air-gapped environment, through a USB thumb drive or other medium: * The Image TAR files. * The YAML files * Tanzu CLI plugins * Tanzu CLI, Kubectl & Carvel Tools - kbld, kapp, ytt and imgpkg
Install Harbor Image Registry
Install Harbor only if you don’t have any existing image repository in your environment.
To install Harbor, deploy an operating system of your choice with the following hardware configuration:
- vCPU: 4
- Memory: 8 GB
- Storage (HDD): 160 GB
Follow the instructions provided in Deploy an Offline Harbor Registry on vSphere to deploy and configure Harbor.
Note: This VM-based harbor deployment is only supported for hosting TKG system images in an internet-restricted or air-gapped environment. To deploy a scalable and highly-available Harbor that can manage large numbers of images for hosted apps in a production environment, deploy the Harbor package to TKG clusters as described in Install Harbor for Service Registry in Creating and Managing TKG 2.3 Workload Clusters with the Tanzu CLI.
Deploy and Configure Bootstrap Machine
The deployment of the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management and workload clusters is facilitated by setting up a bootstrap machine where you install the Tanzu CLI and Kubectl utilities which are used to create and manage the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid instance. This machine also keeps the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid and Kubernetes configuration files for your deployments. The bootstrap machine can be a laptop, host, or server running on Linux, macOS, or Windows that you deploy management and workload clusters from.
The bootstrap machine runs a local kind cluster when Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster deployment is started. Once the kind cluster is fully initialized, the configuration is used to deploy the actual management cluster on the backend infrastructure. After the management cluster is fully configured, the local kind cluster is deleted and future configurations are performed with the Tanzu CLI.
For this deployment, a Photon-based virtual machine is used as the bootstrap machine. For more information about configuring a macOS or a Windows machine, see Install the Tanzu CLI and Other Tools.
The bootstrap machine must meet the following prerequisites:
- A minimum of 6 GB of RAM, 2-core CPU, 160 Storage GB.
- System time is synchronized with a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server.
- Docker and containerd binaries are installed. For instructions on how to install Docker, see the Docker documentation.
- Ensure that the bootstrap VM is connected to Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management network,
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgmanagement.
To install Tanzu CLI, Tanzu Plug-ins, and Kubectl utility on the bootstrap machine, follow the instructions below: 1. Copy Files to bootstrap Machine.
Copy the following files downloaded in Bastion Host through a USB thumb drive or other medium: * Image TAR files * YAML files * Tanzu CLI Plugins
-
Copy following Linux CLI packages from Bastion Host to the bootstrap machine:
- VMware Tanzu CLI v0.90.1 for Linux
- kubectl cluster CLI v1.26.5 for Linux
- Carvel tools - kbld, kapp, ytt & imgpkg
-
Run the following commands to install Tanzu Kubernetes Grid CLI, kubectl CLIs, and Carvel tools:
## Install required packages install tar, zip, unzip, wget ## Install Tanzu Kubernetes Grid CLI tar -xvf tanzu-cli-linux-amd64.tar cd ./v0.90.1/ install tanzu-cli-linux_amd64 /usr/local/bin/tanzu chmod +x /usr/local/bin/tanzu ## Verify Tanzu CLI version # tanzu version version: v0.90.1 buildDate: 2023-06-29 sha: 8945351c -
Log in to the private registry on the offline machine.
docker login <URL> docker login harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw Username: admin Password: WARNING! Your password will be stored unencrypted in /root/.docker/config.json. Configure a credential helper to remove this warning. See https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/login/#credentials-store Login SucceededIf your private registry uses a self-signed certificate, save the CA certificate of the registry in
/etc/docker/certs.d/registry.example.com/ca.crt. -
Upload the Images to the Private Registry.
tanzu isolated-cluster upload-bundle --source-directory <SOURCE-DIRECTORY> --destination-repo <DESTINATION-REGISTRY> --ca-certificate <SECURITY-CERTIFICATE>- SOURCE-DIRECTORY is the path to the location where the image TAR files are stored.
- DESTINATION-REGISTRY is the path to the private registry where the images will be hosted in the air-gapped environment.
- SECURITY-CERTIFICATE is the security certificate of the private registry where the images will be hosted in the proxied or the air-gapped environment.
Example:- t Example: tanzu isolated-cluster upload-bundle --source-directory /home/test/tkg-images/ --destination-repo harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/tkgm-images --ca-certificate /etc/docker/certs.d/harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw-ca.crt -
Upload the CLI plug-ins bundle to harbor repository.
tanzu plugin upload-bundle --tar ./plugin_bundle_tkg_latest.tar.gz --to-repo harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/tkgm-images/ -
Run tanzu plugin source command to set default discovery source to the images uploaded in internal harbor registry.
tanzu plugin source update default --uri harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/tkgm-images/plugin-inventory:latestYou can skip step 4 and 5 if your Bastion host has direct access to the private registry. You can directly upload the files from Bastion to the private registry.
-
Install the kubectl utility.
gunzip kubectl-linux-v1.26.5+vmware.2.gz mv gunzip kubectl-linux-v1.26.5+vmware.2 /usr/local/bin/kubectl && chmod +x /usr/local/bin/kubectl Run the kubectl version --short=true to check that the correct version of kubectl is installed and executable. -
Configure the environment variables.
In an air-gapped environment, if you run the
tanzu initortanzu plugin synccommands, the command hangs and times out after some time with the following error:By default, the Tanzu global config file,
config.yaml, which gets created when you first runtanzu initcommand, points to the repository URL https://projects.registry.vmware.com to fetch the Tanzu plugins for installation. Since there is no Internet in the environment, the commands fails after some time.To ensure that Tanzu Kubernetes Grid always pulls images from the local private registry, run the Tanzu
exportcommand to addTKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORYto the global Tanzu CLI configuration file,~/.config/tanzu/config.yaml.If your image registry is configured with a public signed CA certificate, set the following environment variables:
export TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY=custom-image-repository.io/yourproject export TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY=falseIf your registry solution uses self-signed certificates, also add TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_CA_CERTIFICATE in base64-encoded format to the global Tanzu CLI configuration file. For self-signed certificates, set the following environment variables:
export TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY=custom-image-repository.io/yourproject export TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY=false export TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_CA_CERTIFICATE LS0t[...]tLS0tLQ== # Example root@photon-a17e54311cf [ ~ ]# export TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY=harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/tkgm-images root@photon-a17e54311cf [ ~ ]# export TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY=false root@photon-a17e54311cf [ ~ ]# export TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_CA_CERTIFICATE=LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUZnekNDQTJ1Z0F3SUJBZ0lVUXhvVVV5VnpwUVlkdUlXbStwL3dxZ0JDSFVrd0RRWUpLb1pJaHZjTkFRRUwKQlFBd1VURUxNQWtHQTFVRUJoTUNRMDR4RERBS0JnTlZCQWdNQTFCRlN6RVFNQTRHQTFVRUJ3d0hRbVZwU21sdQpaekVQTUEwR0ExVUVDZ3dHVmsxM1lYSmxNUkV3RHdZRFZRUUREQWhJWVhKaWIzSkRRVEFlRncweU16QTRNRGN3Ck5qVTBOVGRhRncwek16QTRNRFF3TmpVME5UZGFNRkV4Q3pBSkJnTlZCQVlUQWtOT01Rd3dDZ1lEVlFRSURBTlEKUlVzeEVEQU9CZ05WQkFjTUIwSmxhVXBwYm1jeER6QU5CZ05WQkFvTUJsWk5kMkZ5WlRFUk1BOEdBMVVFQXd3SQpTR0Z5WW05eVEwRXdnZ0lpTUEwR0NTcUdTSWIzRFFFQkFRVUFBNElDRHdBd2dnSUtBb0lDQVFDckFtajBVR1lUCjVobm5OeTNIMVdkcUhIejBHbFphWVpGQlhvQVhlWitZa2ljeXJhOFpFeVJCTFBKZVNOcldzMW45dFp1RUg2WDgKM3JJbzUwdzhrZTYwYU9OOU80VlVXZExZKzYxYUxrNlpkNGkzcU9IQTVKSFU1cE5DenU0bThaQ1F1bUp2SzFVSQpwQ1lQNnFtNGxSQUFvWFVzWGZ0S24vRkJ4bGdReTNhUjJ1Y0IzdXA5UndDRllDLzA5TVd5ZjErUmhja3ZvWExRCmppUWx4aHZ0NFpxeG12b09KMi9lbUorTHBqbENZaXBRVkNwN3NpeVM1ZGIvRmw5U1VWSFVlRDhpdzgxKzZTaEEKenRpZXY1U20zbGE0UGw1cUU4Vm9EVEJTUXRpMmQzUXB2M05IR0Z4UUNWMjVTM1BVcWxPQ1Z0dDFtSHRjZEhSUQpTOEN2SE9DVlczRHd5ZXB2Y3M4STJFYlU3M0VQN3JKOEJtL21GQUFwd2F1NXpjMmtxRGJRclMrTjhEeWFpcGY4Ckgxa3FFVlU2VmEvbCtjZHFSbkc1ZWVmM21vT3dKMDBPa2ZqSWtCUExSOC9iZVdDR0R4RVE1RkZlRXhxSTdhNUIKcm1FK25vTTBjMFRQSFp5Z3c4UnZVU3hQbGJ3MFZkVzA5MHdQOHB3WGFGYVBPMmhtT2lvVGJiVkpkMVhqaGRFZAoxWTdmQktYKzl6UUxjb3dlcmF5cDRaSUlSTTNTZnRaZkc5bjErN3pmcVBpamVoTGdiUkUrcHVaaUQwbi9xUXIvClNzOWU5MXZQR1U2NW82VjYvL2Y5MVZmVHJRUmVJV0JWUWNubCtobGpPOVpUeHRRMlVwRnU3TDRwT2RJZ1JHRTgKcDVjZE91TDF1cWltTi8rTW5hckV3K2JFalc0ajF3cnFQUUlEQVFBQm8xTXdVVEFkQmdOVkhRNEVGZ1FVdEozbQpvR3RrcVJiVGl2ZFkzQWxnMTZUOWpCZ3dId1lEVlIwakJCZ3dGb0FVdEozbW9HdGtxUmJUaXZkWTNBbGcxNlQ5CmpCZ3dEd1lEVlIwVEFRSC9CQVV3QXdFQi96QU5CZ2txaGtpRzl3MEJBUXNGQUFPQ0FnRUFUMFBGcUduUjVRdEoKZm1PMTdwSmVDK0IwM3NOVGozS0VzZjUybmJXUnprWm9xNjMrRDZnVURtU3FMMm1RSExRUy9WNWhadmIzZTFCTApDSXpEZmF5cG14K2k3MnlIbVRRNGRBUW5NT2hCUm8rMENVOGpZa0t4TjllN1NhOTlERk0yVE5Bb1pzcEs4ZEVUCmlUa0p2bHlHS2tyellkNEFvczN3dU9uVE85VWxCK1FqQmI4TUVDc3lMR2U4VGxJMk4vOFdwMFMySG1QUHVNeU8KemJ0RUUrSWJXaW1qT1lLRU44cHlUY3plelVnZHpGcXJ3bjVKdWZSejdockV6MnE5ZG9sYm0vTGRNK3pnUHVzZwo0a3lnVjlxWU5KcldvVExXbFJKNzRyQmFOZFpYM3BOV1VGRGtjQ3JkSkloWFFESWdWUDNWa2xJZ21zUUhTU3IrCktJYSt5R1p3MU5hODZML2R0djNrR1ovN2VRMHNHVzVpS3R3VmY5UnBqYTdXL3ZhTTA1OTdFWGNSSGZ2cHRxeFQKcjNOcnFTQmZkTlJtNStXOVh3c0RxNDl3dFdERE52OHNDS2JrenI2Q0JHYUxXSHFGRWtCOHpiTGlJQVBYd2VqaApSOTh5TnY1ZjBzb0ltZlg1R3REY2RMZjd3dGg0UGlvRGloZklrRXVzd0twVGN1WWo3clR0SnFYTFV2b25jZkV0Ck93cytHa2c5L0ZHd0p6ZkJlYUNrNHVXbGw5bC9JanZ6azdydkc0Z1VXa2tMVi9SdmVzbFlEZVlSUXBnYzRybzgKdFFpMThvb3V4RGZuMTlSS2JPVjNtNm5uTlYwdzlHdjZiUGxqbjlRaDB0MWJOaUxwZThJeWhGb0VPOFpVYTBnSApCZ29PbXlGZHQ0VTlQclIvZTdNcWZzM2tQVjZkbmtzPQotLS0tLUVORCBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tIf we reboot the VM , this setting will go to default
-
Install the Tanzu CLI plug-ins.
root@photon-a17e54311cf [ ~ ]# tanzu plugin group search GROUP DESCRIPTION LATEST vmware-tkg/default Plugins for TKG v2.3.0 root@photon-a17e54311cf [ ~ ]# tanzu plugin install --group vmware-tkg/default [i] Installing plugin 'isolated-cluster:v0.30.1' with target 'global' [i] Plugin binary for 'isolated-cluster:v0.30.1' found in cache [i] Installing plugin 'management-cluster:v0.30.1' with target 'kubernetes' [i] Plugin binary for 'management-cluster:v0.30.1' found in cache [i] Installing plugin 'package:v0.30.1' with target 'kubernetes' [i] Plugin binary for 'package:v0.30.1' found in cache [i] Installing plugin 'pinniped-auth:v0.30.1' with target 'global' [i] Plugin binary for 'pinniped-auth:v0.30.1' found in cache [i] Installing plugin 'secret:v0.30.1' with target 'kubernetes' [i] Plugin binary for 'secret:v0.30.1' found in cache [i] Installing plugin 'telemetry:v0.30.1' with target 'kubernetes' [i] Plugin binary for 'telemetry:v0.30.1' found in cache [ok] successfully installed all plugins from group 'vmware-tkg/default:v2.3.0'After installing the tanzu plug-ins, run the
tanzu plugin listcommand to check the plug-in version and installation status. -
Install Carvel tools.
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid uses the following tools from the Carvel open-source project:
- ytt - a command-line tool for templating and patching YAML files. You can also use ytt to collect fragments and piles of YAML into modular chunks for easy re-use.
- kapp - the application deployment CLI for Kubernetes. It allows you to install, upgrade, and delete multiple Kubernetes resources as one application.
- kbld - an image-building and resolution tool.
-
imgpkg - a tool that enables Kubernetes to store configurations and the associated container images as OCI images, and to transfer these images.
-
Install ytt.
gunzip ytt-linux-amd64-v0.45.0+vmware.2.gz chmod ugo+x ytt-linux-amd64-v0.45.0+vmware.2 && mv ./ytt-linux-amd64-v0.45.0+vmware.2 /usr/local/bin/yttRun
ytt --versionto check that the correct version of ytt is installed and executable. -
Install kapp.
gunzip kapp-linux-amd64-v0.55.0+vmware.2.gz chmod ugo+x kapp-linux-amd64-v0.55.0+vmware.2 && mv ./kapp-linux-amd64-v0.55.0+vmware.2 /usr/local/bin/kappRun
kapp --versionto check that the correct version of kapp is installed and executable. -
Install kbld.
gunzip kbld-linux-amd64-v0.37.0+vmware.2.gz chmod ugo+x kbld-linux-amd64-v0.37.0+vmware.2 && mv ./kbld-linux-amd64-v0.37.0+vmware.2 /usr/local/bin/kbldRun
kbld --versionto check that the correct version of kbld is installed and executable. -
Install imgpkg.
gunzip imgpkg-linux-amd64-v0.36.0+vmware.2.gz chmod ugo+x imgpkg-linux-amd64-v0.36.0+vmware.2 && mv ./imgpkg-linux-amd64-v0.36.0+vmware.2 /usr/local/bin/imgpkgRun
imgpkg --versionto check that the correct version of imgpkg is installed and executable.
-
Install yq.
yq a lightweight and portable command-line YAML processor. Click here to download yq.
tar -zxvf yq_linux_amd64.tar.gz mv yq_linux_amd64 /usr/local/bin/Run the
yq -Vcommand to check that the correct version of yq is installed and executable. -
Run the following commands to start the Docker service and enable it to start at boot. Photon OS has Docker installed by default.
## Check Docker service status systemctl status docker ## Start Docker Service systemctl start docker ## To start Docker Service at boot systemctl enable docker -
Execute the following commands to ensure that the bootstrap machine uses cgroup v1.
docker info | grep -i cgroup ## You should see the following Cgroup Driver: cgroupfs -
Create an SSH key-pair.
This is required for Tanzu CLI to connect to vSphere from the bootstrap machine. The public key part of the generated key will be passed during the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster deployment.
### Generate public/Private key pair. ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "email@example.com" ### Add the private key to the SSH agent running on your machine and enter the password you created in the previous step ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa ### If the above command fails, execute "eval $(ssh-agent)" and then rerun the command.Make a note of the public key from the file $home/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. You need this while creating a config file for deploying the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster.
-
If your bootstrap machine runs Linux or Windows Subsystem for Linux, and it has a Linux kernel built after the May 2021 Linux security patch, for example Linux 5.11 and 5.12 with Fedora, run the following command.
sudo sysctl net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_max=131072
Import Base Image Template for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Cluster Deployment
Before you proceed with the management cluster creation, ensure that the base image template is imported into vSphere and is available as a template. To import a base image template into vSphere:
-
Go to the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid downloads page and download a Tanzu Kubernetes Grid OVA for the cluster nodes.
-
For the management cluster, this must be either Photon or Ubuntu based Kubernetes v1.26.5 OVA.
Custom OVA with a custom Tanzu Kubernetes release (TKr) is also supported, as described in Build Machine Images.
- For workload clusters, OVA can have any supported combination of OS and Kubernetes version, as packaged in a Tanzu Kubernetes release.
Ensure that you download the most recent OVA base image templates in the event of security patch releases. You can find updated base image templates that include security patches on the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid product download page.
-
-
In the vSphere client, right-click an object in the vCenter Server inventory and select Deploy OVF template.
-
Select Local file, click the button to upload files, and go to the downloaded OVA file on your local machine.
-
Follow the installer prompts to deploy a VM from the OVA.
-
Click Finish to deploy the VM. When the OVA deployment finishes, right-click the VM and select Template > Convert to Template.
Do not power on the VM before you convert it to a template.
- If using non administrator SSO account: In the VMs and Templates view, right-click the new template, select Add Permission, and assign the tkg-user to the template with the TKG role.
For more information about creating the user and role for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid, see Required Permissions for the vSphere Account.
Management Cluster Configuration Template
The templates include all of the options that are relevant to deploying management clusters on vSphere. You can copy this template and use it to deploy management clusters to vSphere.
- The environment variables that you have set, override values from a cluster configuration file. To use all settings from a cluster configuration file, unset any conflicting environment variables before you deploy the management cluster from the CLI.
- Image repository configuration is very important details which will not be part of default config file when we are creating from TKG UI.
- Insert the key
AVI_NSXT_T1LR. The value of this key is the tier-1 gateway where you have connected thetkg management networknetwork.
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
#! Basic cluster creation configuration
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
CLUSTER_NAME:
CLUSTER_PLAN: <dev/prod>
INFRASTRUCTURE_PROVIDER: vsphere
ENABLE_CEIP_PARTICIPATION: <true/false>
ENABLE_AUDIT_LOGGING: <true/false>
CLUSTER_CIDR: 100.96.0.0/11
SERVICE_CIDR: 100.64.0.0/13
# CAPBK_BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN_TTL: 30m
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
#! vSphere configuration
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
VSPHERE_SERVER:
VSPHERE_USERNAME:
VSPHERE_PASSWORD:
VSPHERE_DATACENTER:
VSPHERE_RESOURCE_POOL:
VSPHERE_DATASTORE:
VSPHERE_FOLDER:
VSPHERE_NETWORK: <tkg-management-network>
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_ENDPOINT: #Leave blank as VIP network is configured in NSX ALB and IPAM is configured with VIP network
# VSPHERE_TEMPLATE:
VSPHERE_SSH_AUTHORIZED_KEY:
VSPHERE_TLS_THUMBPRINT:
VSPHERE_INSECURE: <true/false>
DEPLOY_TKG_ON_VSPHERE7: true
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
#! Node configuration
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# SIZE:
# CONTROLPLANE_SIZE:
# WORKER_SIZE:
# OS_NAME: ""
# OS_VERSION: ""
# OS_ARCH: ""
# VSPHERE_NUM_CPUS: 2
# VSPHERE_DISK_GIB: 40
# VSPHERE_MEM_MIB: 4096
# VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_NUM_CPUS: 2
# VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_DISK_GIB: 40
# VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_MEM_MIB: 8192
# VSPHERE_WORKER_NUM_CPUS: 2
# VSPHERE_WORKER_DISK_GIB: 40
# VSPHERE_WORKER_MEM_MIB: 4096
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
#! NSX Advanced Load Balancer configuration
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
AVI_ENABLE: true
AVI_CONTROL_PLANE_HA_PROVIDER: true
AVI_CONTROLLER:
AVI_USERNAME: ""
AVI_PASSWORD: ""
AVI_CLOUD_NAME:
AVI_SERVICE_ENGINE_GROUP:
AVI_MANAGEMENT_CLUSTER_SERVICE_ENGINE_GROUP:
AVI_DATA_NETWORK:
AVI_DATA_NETWORK_CIDR:
AVI_MANAGEMENT_CLUSTER_VIP_NETWORK_NAME:
AVI_MANAGEMENT_CLUSTER_VIP_NETWORK_CIDR:
AVI_CA_DATA_B64: ""
AVI_LABELS: ""
AVI_NSXT_T1LR: ""
# AVI_DISABLE_STATIC_ROUTE_SYNC: true
# AVI_INGRESS_DEFAULT_INGRESS_CONTROLLER: false
# AVI_INGRESS_SHARD_VS_SIZE: ""
# AVI_INGRESS_SERVICE_TYPE: ""
# AVI_INGRESS_NODE_NETWORK_LIST: ""
# AVI_NAMESPACE: "tkg-system-networking"
# AVI_DISABLE_INGRESS_CLASS: true
# AVI_AKO_IMAGE_PULL_POLICY: IfNotPresent
# AVI_ADMIN_CREDENTIAL_NAME: avi-controller-credentials
# AVI_CA_NAME: avi-controller-ca
#AVI_CONTROLLER_VERSION:# Required for NSX Advanced Load Balancer (ALB) v21.1.x.
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
#! Image repository configuration
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY: ""
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY: false
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_CA_CERTIFICATE: ""
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
#! Machine Health Check configuration
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
ENABLE_MHC:
ENABLE_MHC_CONTROL_PLANE: <true/false>
ENABLE_MHC_WORKER_NODE: <true/flase>
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
#! Identity management configuration
#! ---------------------------------------------------------------------
IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPE: "none"
#! Settings for IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPE: "oidc"
# CERT_DURATION: 2160h
# CERT_RENEW_BEFORE: 360h
# OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_CLIENT_ID:
# OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_CLIENT_SECRET:
# OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_GROUPS_CLAIM: groups
# OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_ISSUER_URL:
# OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_SCOPES: "email,profile,groups"
# OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_USERNAME_CLAIM: email
#! Settings for IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPE: "ldap"
# LDAP_BIND_DN:
# LDAP_BIND_PASSWORD:
# LDAP_HOST:
# LDAP_USER_SEARCH_BASE_DN:
# LDAP_USER_SEARCH_FILTER:
# LDAP_USER_SEARCH_USERNAME: userPrincipalName
# LDAP_USER_SEARCH_ID_ATTRIBUTE: DN
# LDAP_USER_SEARCH_EMAIL_ATTRIBUTE: DN
# LDAP_USER_SEARCH_NAME_ATTRIBUTE:
# LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_BASE_DN:
# LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_FILTER:
# LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_USER_ATTRIBUTE: DN
# LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_GROUP_ATTRIBUTE:
# LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_NAME_ATTRIBUTE: cn
# LDAP_ROOT_CA_DATA_B64:
To create the Management Cluster, run the following command:
tanzu management-cluster create --file config.yaml
-
For a full list of configurable values and to know more about the fields present in the template file, see Create a Management Cluster Configuration File.
-
Create a file using the values provided in the template and save the file with the
.yamlextension. A sample yaml file used for management cluster deployment is provided in the Appendix section for your reference. -
After you have created or updated the cluster configuration file, you can deploy a management cluster by running the
tanzu mc create --file CONFIG-FILEcommand, whereCONFIG-FILEis the name of the configuration file. -
The cluster deployment logs are streamed in the terminal when you run the
tanzu mc createcommand. The first run oftanzu mc createtakes longer than subsequent runs because it has to pull the required Docker images into the image store on your bootstrap machine. Subsequent runs do not require this step, and thus the process is faster. -
While the cluster is being deployed, you will find that a virtual service will be created in NSX Advanced Load Balancer and new SEs will be deployed in vCenter by NSX ALB and the service engines will be mapped to the SE group
sfo01m01segroup01. -
Now, you can access the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster from the bootstrap machine and perform additional tasks such as verifying the management cluster health and deploying the workload clusters, and so on.
-
To get the status of the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster, run the following command:
tanzu management-cluster get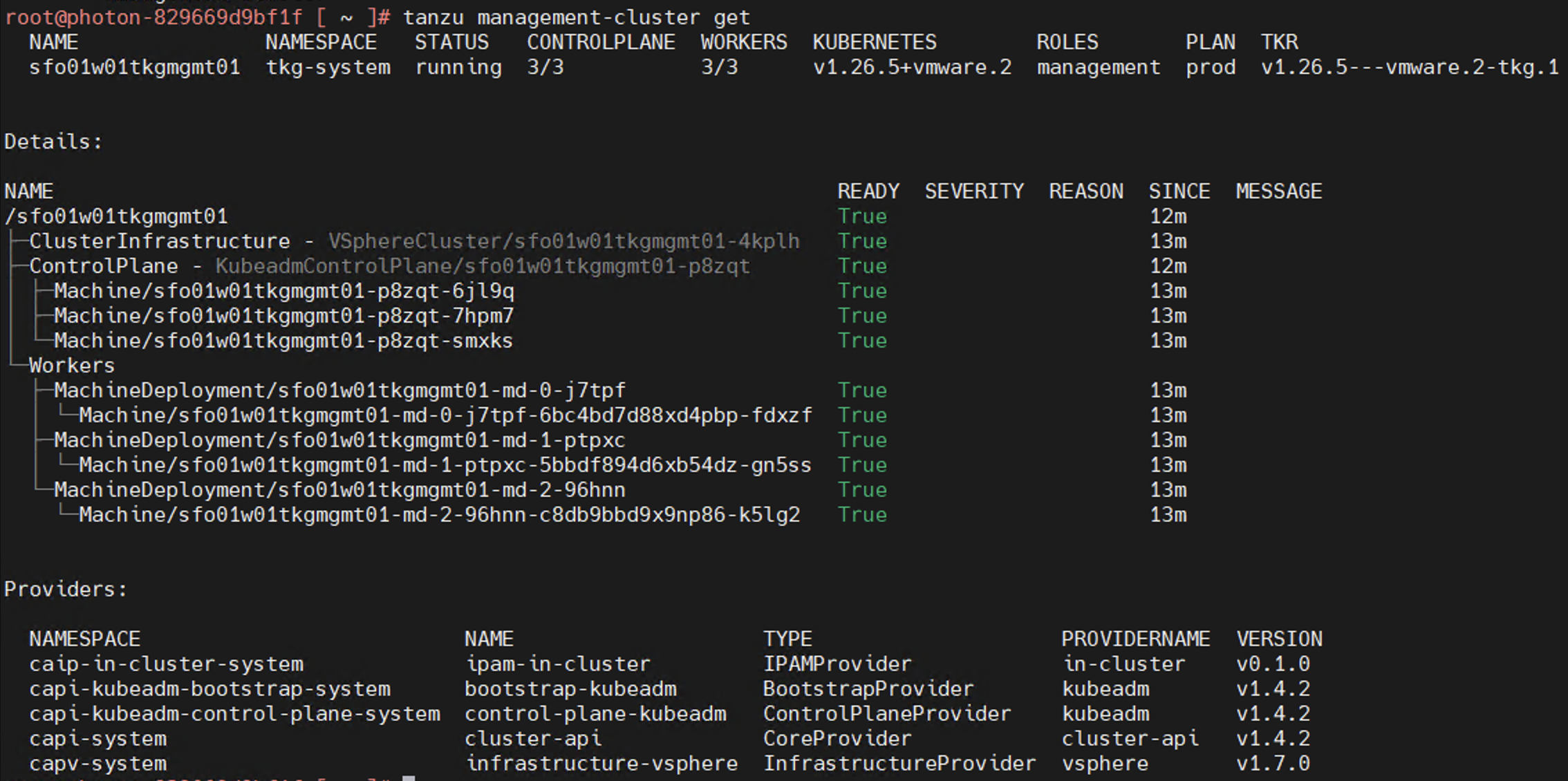
-
Use
kubectl get nodescommand to get the status of the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster nodes.kubectl get nodes
The Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster is successfully deployed and now you can proceed with creating shared services and workload clusters.
Configure AKO Deployment Config (ADC) for Workload Clusters
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management clusters with NSX Advanced Load Balancer are deployed with 2 AKODeploymentConfigs.
install-ako-for-management-cluster: default configuration for management clusterinstall-ako-for-all: default configuration for all workload clusters. By default, all the workload clusters refer to this file for their virtual IP networks and service engine (SE) groups. This ADC configuration does not enable NSX L7 Ingress by default.
As per this Tanzu deployment, create two more ADCs:
-
tanzu-ako-for-shared: Used by shared services cluster to deploy the virtual services inTKG Mgmt SE Groupand the loadbalancer applications inTKG Cluster VIP Network. -
tanzu-ako-for-workload-L7-ingress: Use this ADC only if you would like to enable NSX Advanced Load Balancer L7 ingress on workload cluster. Otherwise, leave the cluster labels empty to apply the network configuration from default ADCinstall-ako-for-all.
Configure AKODeploymentConfig (ADC) for Shared Services Cluster
As per the defined architecture, shared services cluster uses the same control plane and data plane network as the management cluster. Shared services cluster control plane endpoint uses TKG Cluster VIP Network, application loadbalancing uses TKG Cluster VIP Network and the virtual services are deployed in sfo01m01segroup01 SE group. This configuration is enforced by creating a custom AKO Deployment Config (ADC) and applying the respective AVI_LABELS while deploying the shared services cluster.
The format of the AKODeploymentConfig YAML file is as follows:
apiVersion: networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: AKODeploymentConfig
metadata:
finalizers:
- ako-operator.networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com
generation: 2
name: <Unique name of AKODeploymentConfig>
spec:
adminCredentialRef:
name: nsx-alb-controller-credentials
namespace: tkg-system-networking
certificateAuthorityRef:
name: nsx-alb-controller-ca
namespace: tkg-system-networking
cloudName: <NAME OF THE CLOUD in ALB>
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
<KEY>: <VALUE>
controlPlaneNetwork:
cidr: <TKG-Cluster-VIP-CIDR>
Name: <TKG-Cluster-VIP-Network>
controller: <NSX ALB CONTROLLER IP/FQDN>
dataNetwork:
cidr: <TKG-Mgmt-Data-VIP-CIDR>
name: <TKG-Mgmt-Data-VIP-Name>
extraConfigs:
cniPlugin: antrea
disableStaticRouteSync: true
ingress:
defaultIngressController: false
disableIngressClass: true
nodeNetworkList:
- networkName: <TKG-Mgmt-Network>
serviceEngineGroup: <Mgmt-Cluster-SEG>
The sample AKODeploymentConfig with sample values in place is as follows. You must add the respective NSX ALB label type=shared-services while deploying shared services cluster to enforce this network configuration.
- cloud:
sfo01w01vc01 - service engine group:
sfo01m01segroup01 - Control Plane network:
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip - VIP/data network:
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip - Node Network:
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgmanagement
apiVersion: networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: AKODeploymentConfig
metadata:
generation: 3
name: tanzu-ako-for-shared
spec:
adminCredentialRef:
name: avi-controller-credentials
namespace: tkg-system-networking
certificateAuthorityRef:
name: avi-controller-ca
namespace: tkg-system-networking
cloudName: sfo01w01vc01
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
type: shared-services
controlPlaneNetwork:
cidr: 172.16.80.0/24
name: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip
controller: 172.16.10.10
controllerVersion: 22.1.3
dataNetwork:
cidr: 172.16.80.0/24
name: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip
extraConfigs:
disableStaticRouteSync: false
ingress:
defaultIngressController: false
disableIngressClass: true
nodeNetworkList:
- networkName: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgmanagement
networksConfig:
nsxtT1LR: /infra/tier-1s/sfo01w01tier1
serviceEngineGroup: sfo01m01segroup01
For a single VIP Network Architecture, see Single VIP Nertwork Architecture - Shared Service Cluster ADC file.
After you have the AKO configuration file ready, use the kubectl command to set the context to Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster and create the ADC:
# kubectl config use-context sfo01w01tkgmgmt01-admin@sfo01w01tkgmgmt01
Switched to context "sfo01w01tkgmgmt01-admin@sfo01w01tkgmgmt01".
# kubectl apply -f ako-shared-services.yaml
akodeploymentconfig.networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/tanzu-ako-for-shared created
Use the following command to list all AKODeploymentConfig created under the management cluster:
# kubectl get adc
NAME AGE
install-ako-for-all 21h
install-ako-for-management-cluster 21h
tanzu-ako-for-shared 113s
Configure AKO Deployment Config (ADC) for Workload Cluster to Enable NSX ALB L7 Ingress with NodePortLocal Mode
VMware recommends using NSX Advanced Load Balancer L7 ingress with NodePortLocal mode for the L7 application load balancing. This is enabled by creating a custom ADC with ingress settings enabled, and then applying the AVI_LABELS while deploying the workload cluster.
As per the defined architecture, workload cluster cluster control plane endpoint uses TKG Cluster VIP Network, application loadbalancing uses TKG Workload VIP Network and the virtual services are deployed in sfo01w01segroup01 SE group.
Below are the changes in ADC Ingress section when compare to the default ADC.
-
disableIngressClass: Set to
falseto enable NSX ALB L7 Ingress. -
nodeNetworkList: Provide the values for TKG workload network name and CIDR.
-
serviceType: L7 Ingress type, recommended to use
NodePortLocal -
shardVSSize: Virtual service size
The format of the AKODeploymentConfig YAML file for enabling NSX ALB L7 Ingress is as follows:
apiVersion: networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: AKODeploymentConfig
metadata:
name: <unique-name-for-adc>
spec:
adminCredentialRef:
name: NSXALB-controller-credentials
namespace: tkg-system-networking
certificateAuthorityRef:
name: NSXALB-controller-ca
namespace: tkg-system-networking
cloudName: <cloud name configured in nsx alb>
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
<KEY>: <value>
controller: <ALB-Controller-IP/FQDN>
controlPlaneNetwork:
cidr: <TKG-Cluster-VIP-Network-CIDR>
name: <TKG-Cluster-VIP-Network-CIDR>
dataNetwork:
cidr: <TKG-Workload-VIP-network-CIDR>
name: <TKG-Workload-VIP-network-CIDR>
extraConfigs:
cniPlugin: antrea
disableStaticRouteSync: false # required
ingress:
disableIngressClass: false # required
nodeNetworkList: # required
- networkName: <TKG-Workload-Network>
cidrs:
- <TKG-Workload-Network-CIDR>
serviceType: NodePortLocal # required
shardVSSize: MEDIUM # required
serviceEngineGroup: <Workload-Cluster-SEG>
The AKODeploymentConfig with sample values in place is as follows. You should add the respective NSX ALB label workload-l7-enabled=true while deploying shared services cluster to enforce this network configuration.
- cloud:
sfo01w01vc01 - service engine group:
sfo01w01segroup01 - Control Plane network:
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip - VIP/data network:
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvip - Node Network:
sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkload
apiVersion: networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: AKODeploymentConfig
metadata:
generation: 3
name: tanzu-ako-for-workload-L7-ingress
spec:
adminCredentialRef:
name: avi-controller-credentials
namespace: tkg-system-networking
certificateAuthorityRef:
name: avi-controller-ca
namespace: tkg-system-networking
cloudName: sfo01w01vc01
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
workload-l7-enabled: "true"
controlPlaneNetwork:
cidr: 172.16.80.0/24
name: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip
controller: 172.16.10.11
controllerVersion: 22.1.3
dataNetwork:
cidr: 172.16.70.0/24
name: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvip
extraConfigs:
disableStaticRouteSync: true
ingress:
defaultIngressController: true
disableIngressClass: false
serviceType: NodePortLocal
shardVSSize: MEDIUM
nodeNetworkList:
- networkName: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkload
cidrs:
- 172.16.60.0/24
networksConfig:
nsxtT1LR: /infra/tier-1s/sfo01w01tier2
serviceEngineGroup: sfo01w01segroup01
For a single VIP Network Architecture, see Single VIP Nertwork Architecture - Workload Cluster ADC file.
Use the kubectl command to set the context to Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management cluster and create the ADC:
# kubectl config use-context sfo01w01tkgmgmt01-admin@sfo01w01tkgmgmt01
Switched to context "sfo01w01tkgmgmt01-admin@sfo01w01tkgmgmt01".
# kubectl apply -f workload-adc-l7.yaml
akodeploymentconfig.networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/tanzu-ako-for-workload-l7-ingress created
Use the following command to list all AKODeploymentConfig created under the management cluster:
# kubectl get adc
NAME AGE
install-ako-for-all 22h
install-ako-for-management-cluster 22h
tanzu-ako-for-shared 82m
tanzu-ako-for-workload-l7-ingress 25s
Now that you have successfully created the AKO deployment config, you need to apply the cluster labels while deploying the workload clusters to enable NSX Advanced Load Balancer L7 Ingress with the NodePortLocal mode.
Deploy Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Shared Services Cluster
Each Tanzu Kubernetes Grid instance can have only one shared services cluster. Create a shared services cluster if you intend to deploy Harbor.
The procedures for deploying a shared services cluster and workload cluster are almost the same. A key difference is that for the shared service cluster you add the tanzu-services label to the shared services cluster, as its cluster role. This label identifies the shared services cluster to the management cluster and workload clusters.
Shared services cluster uses the custom ADC tanzu-ako-for-shared created earlier to apply the network settings similar to the management cluster. This is enforced by applying the AVI_LABEL type:shared-services while deploying the shared services cluster.
Deployment of the shared services cluster is done by creating a YAML file and invoking the tanzu cluster create -f <file-name> command. The YAML file used for shared services deployment is smaller compared to the YAML used for the management cluster deployment because, you don’t need to define the AVI fields except AVI_CONTROL_PLANE_HA_PROVIDER & AVI_LABELS in the YAML.
Image repository configuration is very important details.
A sample yaml for shared services cluster deployment is given below:
CLUSTER_NAME: sfo01w01tkgshared01
CLUSTER_PLAN: prod
INFRASTRUCTURE_PROVIDER: vsphere
ENABLE_CEIP_PARTICIPATION: "true"
ENABLE_AUDIT_LOGGING: "true"
CLUSTER_CIDR: 100.96.0.0/11
SERVICE_CIDR: 100.64.0.0/13
VSPHERE_SERVER: sfo01w01vc01.sfo01.rainpole.local
VSPHERE_USERNAME: administrator@vsphere.local
VSPHERE_PASSWORD: <encoded:Vk13YXJlMSE=>
VSPHERE_DATACENTER: /sfo01w01dc01
VSPHERE_RESOURCE_POOL: /sfo01w01dc01/host/sfo01w01cluster01/Resources/tkg-sharedsvc-components
VSPHERE_DATASTORE: /sfo01w01dc01/datastore/vsanDatastore
VSPHERE_FOLDER: /sfo01w01dc01/vm/tkg-sharedsvc-components
VSPHERE_NETWORK: /sfo01w01dc01/network/sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgshared
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_ENDPOINT: #Leave blank as VIP network is configured in NSX ALB and IPAM is configured with VIP network
VSPHERE_SSH_AUTHORIZED_KEY: ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAACAQDrPqkVaPpNxHcKxukYroV6LcCTuRK9NDyygbsAr/P73jEeWIcC+SU4tRpOZks2+BoduUDzdrsfm/Uq/0uj9LuzqIZKAzA1iQ5DtipVzROqeTuAXJVCMZc6RPgQSZofLBo1Is85M/IrBS20OMALwjukMdwotKKFwL758l51FVsKOT+MUSW/wJLKTv3l0KPObgSRTMUQdQpoG7ONcMNG2VkBMfgaK44cL7vT0/0Mv/Fmf3Zd59ZaWvX28ZmGEjRx8kOm1j/os61Y+kOvl1MTv8wc85rYusRuP2Uo5UM4kUTdhSTFasw6TLhbSWicKORPi3FYklvS70jkQFse2WsvmtFG5xyxE/rzDGHloud9g2bQ7Tx0rtWWoRCCC8Sl/vzCjgZfDQXwKXoMP0KbcYHZxSA3zY2lXBlhNtZtyKlynnhr97EaWsm3b9fvhJMmKW5ylkmk7+4Bql7frJ4bOOR4+hHv57Q8XFOYdLGQPGv03RUFQwFE6a0a6qWAvmVmoh8+BmlGOfx7WYpp8hkyGOdtQz8ZJeSOyMT6ztLHbY/WqDwEvKpf1dJy93w8fDmz3qXHpkpdnA0t4TiCfizlBk15ZI03TLi4ELoFvso9We13dGClHDDyv0Dm87uaACC+fyAT5JPbZpAcCw8rm/yTuZ8awtR0LEzJUqNJjX/5OX7Bf45h9w== email@example.com
VSPHERE_TLS_THUMBPRINT: DC:FA:81:1D:CA:08:21:AB:4E:15:BD:2B:AE:12:2C:6B:CA:65:49:B8
VSPHERE_INSECURE: "false"
OS_NAME: photon
OS_VERSION: "3"
OS_ARCH: amd64
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_NUM_CPUS: 2
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_DISK_GIB: 40
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_MEM_MIB: 8192
VSPHERE_WORKER_NUM_CPUS: 2
VSPHERE_WORKER_DISK_GIB: 40
VSPHERE_WORKER_MEM_MIB: 8192
AVI_CONTROL_PLANE_HA_PROVIDER: "true"
AVI_LABELS: |
'type': 'shared-services'
ENABLE_MHC: "true"
IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPE: "none"
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY: harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/tkgm-images
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY: false
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_CA_CERTIFICATE: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUZnekNDQTJ1Z0F3SUJBZ0lVUXhvVVV5VnpwUVlkdUlXbStwL3dxZ0JDSFVrd0RRWUpLb1pJaHZjTkFRRUwKQlFBd1VURUxNQWtHQTFVRUJoTUNRMDR4RERBS0JnTlZCQWdNQTFCRlN6RVFNQTRHQTFVRUJ3d0hRbVZwU21sdQpaekVQTUEwR0ExVUVDZ3dHVmsxM1lYSmxNUkV3RHdZRFZRUUREQWhJWVhKaWIzSkRRVEFlRncweU16QTRNRGN3Ck5qVTBOVGRhRncwek16QTRNRFF3TmpVME5UZGFNRkV4Q3pBSkJnTlZCQVlUQWtOT01Rd3dDZ1lEVlFRSURBTlEKUlVzeEVEQU9CZ05WQkFjTUIwSmxhVXBwYm1jeER6QU5CZ05WQkFvTUJsWk5kMkZ5WlRFUk1BOEdBMVVFQXd3SQpTR0Z5WW05eVEwRXdnZ0lpTUEwR0NTcUdTSWIzRFFFQkFRVUFBNElDRHdBd2dnSUtBb0lDQVFDckFtajBVR1lUCjVobm5OeTNIMVdkcUhIejBHbFphWVpGQlhvQVhlWitZa2ljeXJhOFpFeVJCTFBKZVNOcldzMW45dFp1RUg2WDgKM3JJbzUwdzhrZTYwYU9OOU80VlVXZExZKzYxYUxrNlpkNGkzcU9IQTVKSFU1cE5DenU0bThaQ1F1bUp2SzFVSQpwQ1lQNnFtNGxSQUFvWFVzWGZ0S24vRkJ4bGdReTNhUjJ1Y0IzdXA5UndDRllDLzA5TVd5ZjErUmhja3ZvWExRCmppUWx4aHZ0NFpxeG12b09KMi9lbUorTHBqbENZaXBRVkNwN3NpeVM1ZGIvRmw5U1VWSFVlRDhpdzgxKzZTaEEKenRpZXY1U20zbGE0UGw1cUU4Vm9EVEJTUXRpMmQzUXB2M05IR0Z4UUNWMjVTM1BVcWxPQ1Z0dDFtSHRjZEhSUQpTOEN2SE9DVlczRHd5ZXB2Y3M4STJFYlU3M0VQN3JKOEJtL21GQUFwd2F1NXpjMmtxRGJRclMrTjhEeWFpcGY4Ckgxa3FFVlU2VmEvbCtjZHFSbkc1ZWVmM21vT3dKMDBPa2ZqSWtCUExSOC9iZVdDR0R4RVE1RkZlRXhxSTdhNUIKcm1FK25vTTBjMFRQSFp5Z3c4UnZVU3hQbGJ3MFZkVzA5MHdQOHB3WGFGYVBPMmhtT2lvVGJiVkpkMVhqaGRFZAoxWTdmQktYKzl6UUxjb3dlcmF5cDRaSUlSTTNTZnRaZkc5bjErN3pmcVBpamVoTGdiUkUrcHVaaUQwbi9xUXIvClNzOWU5MXZQR1U2NW82VjYvL2Y5MVZmVHJRUmVJV0JWUWNubCtobGpPOVpUeHRRMlVwRnU3TDRwT2RJZ1JHRTgKcDVjZE91TDF1cWltTi8rTW5hckV3K2JFalc0ajF3cnFQUUlEQVFBQm8xTXdVVEFkQmdOVkhRNEVGZ1FVdEozbQpvR3RrcVJiVGl2ZFkzQWxnMTZUOWpCZ3dId1lEVlIwakJCZ3dGb0FVdEozbW9HdGtxUmJUaXZkWTNBbGcxNlQ5CmpCZ3dEd1lEVlIwVEFRSC9CQVV3QXdFQi96QU5CZ2txaGtpRzl3MEJBUXNGQUFPQ0FnRUFUMFBGcUduUjVRdEoKZm1PMTdwSmVDK0IwM3NOVGozS0VzZjUybmJXUnprWm9xNjMrRDZnVURtU3FMMm1RSExRUy9WNWhadmIzZTFCTApDSXpEZmF5cG14K2k3MnlIbVRRNGRBUW5NT2hCUm8rMENVOGpZa0t4TjllN1NhOTlERk0yVE5Bb1pzcEs4ZEVUCmlUa0p2bHlHS2tyellkNEFvczN3dU9uVE85VWxCK1FqQmI4TUVDc3lMR2U4VGxJMk4vOFdwMFMySG1QUHVNeU8KemJ0RUUrSWJXaW1qT1lLRU44cHlUY3plelVnZHpGcXJ3bjVKdWZSejdockV6MnE5ZG9sYm0vTGRNK3pnUHVzZwo0a3lnVjlxWU5KcldvVExXbFJKNzRyQmFOZFpYM3BOV1VGRGtjQ3JkSkloWFFESWdWUDNWa2xJZ21zUUhTU3IrCktJYSt5R1p3MU5hODZML2R0djNrR1ovN2VRMHNHVzVpS3R3VmY5UnBqYTdXL3ZhTTA1OTdFWGNSSGZ2cHRxeFQKcjNOcnFTQmZkTlJtNStXOVh3c0RxNDl3dFdERE52OHNDS2JrenI2Q0JHYUxXSHFGRWtCOHpiTGlJQVBYd2VqaApSOTh5TnY1ZjBzb0ltZlg1R3REY2RMZjd3dGg0UGlvRGloZklrRXVzd0twVGN1WWo3clR0SnFYTFV2b25jZkV0Ck93cytHa2c5L0ZHd0p6ZkJlYUNrNHVXbGw5bC9JanZ6azdydkc0Z1VXa2tMVi9SdmVzbFlEZVlSUXBnYzRybzgKdFFpMThvb3V4RGZuMTlSS2JPVjNtNm5uTlYwdzlHdjZiUGxqbjlRaDB0MWJOaUxwZThJeWhGb0VPOFpVYTBnSApCZ29PbXlGZHQ0VTlQclIvZTdNcWZzM2tQVjZkbmtzPQotLS0tLUVORCBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0t
To create Workload Cluster, run the following command:
tanzu cluster create --file config.yaml
Cluster creation takes approximately 15-20 minutes to complete. Verify the health of the cluster and validate the cluster labels applied.
-
Connect to the Tanzu Management Cluster context and verify the cluster labels for the Shared Service cluster.
## verify the Shared Service cluster creation tanzu cluster list NAME NAMESPACE STATUS CONTROLPLANE WORKERS KUBERNETES ROLES PLAN TKR sfo01w01tkgshared01 default running 3/3 3/3 v1.26.5+vmware.2 <none> prod v1.26.5---vmware.2-tkg.1 ## Connect to tkg management cluster kubectl config use-context sfo01w01tkgmgmt01-admin@sfo01w01tkgmgmt01 ## Add the tanzu-services label to the shared services cluster as its cluster role. In the following command "sfo01w01tkgshared01” is the name of the shared service cluster kubectl label cluster.cluster.x-k8s.io/sfo01w0tkgshared01 cluster-role.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/tanzu-services="" --overwrite=true cluster.cluster.x-k8s.io/sfo01w0tkgshared01 labeled ## Validate AVI_LABELS applied to shared serice cluster kubectl get cluster sfo01w0tkgshared01 --show-labels NAME PHASE AGE VERSION LABELS sfo01w0tkgshared01 Provisioned 105m cluster-role.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/tanzu-services=,networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/avi=tanzu-ako-for-shared,tanzuKubernetesRelease=v1.26.5---vmware.2-tkg.1,tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/cluster-name=sfo01w0tkgshared01,type=shared-services -
Connect to admin context of the Shared Service cluster using the following commands and validate the ako pod status.
## Use the following command to get the admin context of Service Service Cluster. tanzu cluster kubeconfig get sfo01w0tkgshared01 --admin Credentials of cluster 'sfo01w0tkgshared01' have been saved You can now access the cluster by running 'kubectl config use-context sfo01w0tkgshared01-admin@sfo01w0tkgshared01' ## Use the following command to use the context of Shared Service Cluster kubectl config use-context sfo01w0tkgshared01-admin@sfo01w0tkgshared01 Switched to context "sfo01w0tkgshared01-admin@sfo01w0tkgshared01". # Verify that ako pod gets deployed in avi-system namespace kubectl get pods -n avi-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ako-0 1/1 Running 0 73m # verify the nodes and pods status by running the command: kubectl get nodes -o wide kubectl get pods -A
Now, the shared services cluster is successfully created.
Deploy Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Workload Cluster
The workload cluster is deployed by using a YAML file similar to the shared services cluster YAML file but customized for the workload cluster placement objects.
The following is a sample YAML for deploying the workload cluster:
CLUSTER_CIDR: 100.96.0.0/11
SERVICE_CIDR: 100.64.0.0/13
CLUSTER_PLAN: prod
ENABLE_CEIP_PARTICIPATION: 'false'
ENABLE_MHC: 'true'
IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPE: none
INFRASTRUCTURE_PROVIDER: vsphere
TKG_HTTP_PROXY_ENABLED: 'false'
AVI_CONTROL_PLANE_HA_PROVIDER: "true"
CLUSTER_NAME: sfo01w01tkgworkload01
DEPLOY_TKG_ON_VSPHERE7: 'false'
OS_ARCH: amd64
OS_NAME: photon
OS_VERSION: "3"
AVI_LABELS: |
'workload-l7-enabled': 'true'
VSPHERE_DATACENTER: /sfo01w01dc01
VSPHERE_DATASTORE: /sfo01w01dc01/datastore/vsanDatastore
VSPHERE_FOLDER: /sfo01w01dc01/vm/tkg-workload01-components
VSPHERE_INSECURE: "true"
VSPHERE_NETWORK: /sfo01w01dc01/network/sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkload
VSPHERE_PASSWORD: <encoded:Vk13YXJlMSE=>
VSPHERE_RESOURCE_POOL: /sfo01w01dc01/host/sfo01w01cluster01/Resources/tkg-workload01-components
VSPHERE_SERVER: sfo01w01vc01.sfo01.rainpole.local
VSPHERE_SSH_AUTHORIZED_KEY: ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAACAQDrPqkVaPpNxHcKxukYroV6LcCTuRK9NDyygbsAr/P73jEeWIcC+SU4tRpOZks2+BoduUDzdrsfm/Uq/0uj9LuzqIZKAzA1iQ5DtipVzROqeTuAXJVCMZc6RPgQSZofLBo1Is85M/IrBS20OMALwjukMdwotKKFwL758l51FVsKOT+MUSW/wJLKTv3l0KPObgSRTMUQdQpoG7ONcMNG2VkBMfgaK44cL7vT0/0Mv/Fmf3Zd59ZaWvX28ZmGEjRx8kOm1j/os61Y+kOvl1MTv8wc85rYusRuP2Uo5UM4kUTdhSTFasw6TLhbSWicKORPi3FYklvS70jkQFse2WsvmtFG5xyxE/rzDGHloud9g2bQ7Tx0rtWWoRCCC8Sl/vzCjgZfDQXwKXoMP0KbcYHZxSA3zY2lXBlhNtZtyKlynnhr97EaWsm3b9fvhJMmKW5ylkmk7+4Bql7frJ4bOOR4+hHv57Q8XFOYdLGQPGv03RUFQwFE6a0a6qWAvmVmoh8+BmlGOfx7WYpp8hkyGOdtQz8ZJeSOyMT6ztLHbY/WqDwEvKpf1dJy93w8fDmz3qXHpkpdnA0t4TiCfizlBk15ZI03TLi4ELoFvso9We13dGClHDDyv0Dm87uaACC+fyAT5JPbZpAcCw8rm/yTuZ8awtR0LEzJUqNJjX/5OX7Bf45h9w== email@example.com
VSPHERE_TLS_THUMBPRINT: ""
VSPHERE_USERNAME: administrator@vsphere.local
ENABLE_AUDIT_LOGGING: true
ENABLE_DEFAULT_STORAGE_CLASS: true
ENABLE_AUTOSCALER: false
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_NUM_CPUS: 2
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_DISK_GIB: 40
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_MEM_MIB: 8192
VSPHERE_WORKER_NUM_CPUS: 2
VSPHERE_WORKER_DISK_GIB: 40
VSPHERE_WORKER_MEM_MIB: 8192
WORKER_MACHINE_COUNT: 3
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY: harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/tkgm-images
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY: false
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_CA_CERTIFICATE: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUZnekNDQTJ1Z0F3SUJBZ0lVT2hDeStrNUtDRGRKSUl2QS9IV1ZXKzdiYUVrd0RRWUpLb1pJaHZjTkFRRUwKQlFBd1VURUxNQWtHQTFVRUJoTUNRMDR4RERBS0JnTlZCQWdNQTFCRlN6RVFNQTRHQTFVRUJ3d0hRbVZwU21sdQpaekVQTUEwR0ExVUVDZ3dHVmsxM1lYSmxNUkV3RHdZRFZRUUREQWhJWVhKaWIzSkRRVEFlRncweU16QTNNVGd4Ck5qVXdORFZhRncwek16QTNNVFV4TmpVd05EVmFNRkV4Q3pBSkJnTlZCQVlUQWtOT01Rd3dDZ1lEVlFRSURBTlEKUlVzeEVEQU9CZ05WQkFjTUIwSmxhVXBwYm1jeER6QU5CZ05WQkFvTUJsWk5kMkZ5WlRFUk1BOEdBMVVFQXd3SQpTR0Z5WW05eVEwRXdnZ0lpTUEwR0NTcUdTSWIzRFFFQkFRVUFBNElDRHdBd2dnSUtBb0lDQVFDUVlWMFhQTWFlClZDQU5SdUMzMFBEeERvMVFIRVRQdmUyQVhUQWsxVXkra09JOUpWQzFUek9RUW42YjFtbmNLUzBsM2cyR3JDNnUKeFNKR25NNEJyMWxsalZwNHh5TU1LcndXdTVkZzRQZXBqempLeVFuaVNkcEx4TThOYnNlU0JjN3U0YWNHNWVRcgpxSHZRTy8zK0k1cTI1SXE1Mi9EaEZiSjdZbllVTTRuc2c3TUZEU2xqRnVlYTNTTytORms5OFI5bmh3RnpOTXRYCkFFM28rL0t3SjRlTmwyRTJGUHhOUW5nTDhMWG8wUWE4OXFCbXdjMmx6eGFCc1N3VDNpOWlMQ2JLK0pabzAvZHAKaXRwZGcrZHNpZ1dUcWRFekErMG12aCtlNW9iaG43UXo2VzJpb3pRMWZGcVRKZ09Jd1VFZ2srdG5SZWxhZFBFQQpKaUcvQVBncGdQY0ZleDExeUFJYUdUNnRNOVlPV3VMRk5mV1FCNTBzVWRRZlJaUlk5cUxheG1uR1c2TWhDMEsrCkFIcmgvUmxJa2g5cVFVZmoxTUpLdFNrZzJBQVRRZ3RVWkY2TG1nei9XK1p6aU0xOG1HY1pRU3UzUWVHWElSL1IKWjF5VzcrTWhUQ2Q0ZHRiU1FzRFBGZEhaazZVVXhlOE40MjV4cTFBeG5PNCtSR3dBTG96RS9YWk1zbnNZaDhiego5UHpXSFIxN2E5UGJ1L1l6c2NDNE9qN1dJVlY4UGtWREptK0xaelhDUU5IL2g1Y1phSzZhSXU4d0NLSG5KdE42CnA4RUpsWkliZ3RTOEl5eVJqQStycUZ2QUtXS2tjYVEwUVduWjB6MjBTVk9vYVg2bHNlbnBaZmpyS1RnV3hUdncKS01tTkQyc0NkVU91MnlkWHpMVWRRUDBDb25VN3V3bnViUUlEQVFBQm8xTXdVVEFkQmdOVkhRNEVGZ1FVS1FGegpOcjdwYzZndHdOUitCVXhud1h1TVY5NHdId1lEVlIwakJCZ3dGb0FVS1FGek5yN3BjNmd0d05SK0JVeG53WHVNClY5NHdEd1lEVlIwVEFRSC9CQVV3QXdFQi96QU5CZ2txaGtpRzl3MEJBUXNGQUFPQ0FnRUFEay85UjVDYkhrek8KZGdQbXFPVVlqUnVUcWdtcWdqbUlhM2VWNG51NzdmNGpRZWNwcnJJTzcrbk1vN0RrTHNBQURyNVdjL0xFdTBlTAp2N0c2U3Rsbzd6dVVpRlVmbERvUndsaFRnMXdyRDBxcmNxendUTUFTWVh2dWxLOWgvU05ySEdmR2hJL1Q5TXBPCm1leS85WkY1ZmdOTC80b2lvQ0lPVXFkQ2luUWhCaEFGQWJ5YWUrNHI4dXkzcXB6VDQ2ZXVRY040YmVTczBoaFUKNnpwRWpRU05mWjJOUWRSbHhISWlPT1pKZ1pmYXlZa3Ard2hqT3ZTL09Vdm5NR0tNNk1hckk4L3QzVVBhNHE1ZQpLVU9PS01Ma3RRWjA5a3o1VndZWmFuNk4yL010U09hT28zdmx6b0ZXSC9LdFdUZFhxcmppRmN6UmFORElxZEExCkJXR2xYcUJsUTdHWjRTazBHSzE1cENJUU9QZTZ4dEprVW9GSnV4SDJ5TW9tUWlMbFdQdE9obllSWkhEWUpjMkcKem81SFVkM0lhNnlROUMySlZzcGdXcFhYeWtsVmJPb0treVFvWVorWU1rdGt5dDJnaG52S1ZNTm5PUXdCM2dpcgpBMVZTY29UUS82ZEREcFl4MytwVTZGSXpRdXgzdDRkZUZOWU8zd3BjSksrbS9PSUZFZlNGbXdPTFJ0NTMzU1RiCk94dzJKdzZPQ0tobzl0TUZBNGR6czBUS3R6NE9QUTlTb2RxZDlsNlZNbnprY1JlcFdHd0wzQ0JjRHBCdlFQNjAKWVQydHAwRGEwSmZ3cExSdk55WE5xQXZZZUUydHEvTG9EcG1lcnoyYUZHR3c1VDZsTDhwMXZYeUdEYmw2bEVIawpJRXBQUWExWk8vVW5HKzdUeEZ1OHhHV21YVXVFcEQ0PQotLS0tLUVORCBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0t
To create Workload Cluster, run the following command:
tanzu cluster create --file config.yaml
The Cluster creation takes 15-20 minutes to complete. Verify the health of the cluster and apply the labels.
After the Workload cluster is created, verify the cluster labels and ako pod status.
-
Connect to the Tanzu Management Cluster context and verify the cluster labels for the workload cluster.
## verify the workload cluster creation tanzu cluster list NAME NAMESPACE STATUS CONTROLPLANE WORKERS KUBERNETES ROLES PLAN TKR sfo01w01tkgshared01 default running 3/3 3/3 v1.26.5+vmware.2 <none> prod v1.26.5---vmware.2-tkg.1 sfo01w01tkgworkload01 default running 3/3 3/3 v1.26.5+vmware.2 <none> prod v1.26.5---vmware.2-tkg.1 ## Connect to tkg management cluster kubectl config use-context sfo01w01tkgmgmt01-admin@sfo01w01tkgmgmt01 ## Validate AVI_LABELS applied to workload cluster kubectl get cluster sfo01w01workload01 --show-labels NAME PHASE AGE VERSION LABELS sfo01w01tkgworkload01 Provisioned 105m networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/avi=tanzu-ako-for-workload-l7-ingress,tanzuKubernetesRelease=v1.26.5---vmware.2-tkg.1,tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/cluster-name=sfo01w01tkgworkload01,workload-l7-enabled=true -
Connect to admin context of the workload cluster using the following commands and validate the ako pod status.
## Use the following command to get the admin context of workload Cluster. tanzu cluster kubeconfig get sfo01w01tkgworkload01 --admin Credentials of cluster 'sfo01w01tkgworkload01' have been saved You can now access the cluster by running 'kubectl config use-context sfo01w01tkgworkload01-admin@sfo01w01workload01' ## Use the following command to use the context of workload Cluster kubectl config use-context sfo01w01tkgworkload01-admin@sfo01w01workload01 Switched to context "sfo01w01tkgworkload01-admin@sfo01w01workload01". # Verify that ako pod gets deployed in avi-system namespace kubectl get pods -n avi-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ako-0 1/1 Running 0 73m # verify the nodes and pods status by running the command: kubectl get nodes -o wide kubectl get pods -A
You can see that the workload cluster is successfully deployed and the AKO pod is deployed on the cluster. You can now deploy user-managed packages on this cluster.
Deploy User-Managed Packages
User-managed packages are installed after workload cluster creation. These packages extend the core functionality of Kubernetes clusters created by Tanzu Kubernetes Grid.
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid includes the following user-managed packages. These packages provide in-cluster and shared services to the Kubernetes clusters that are running in your Tanzu Kubernetes Grid environment.
Installing and Managing Packages with the Tanzu CLI
| Function | Package | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Certificate Management | Cert Manager | Workload and shared services cluster |
| Container registry | Harbor | Shared services cluster |
| Ingress control | Contour | Workload and shared services cluster |
| Log forwarding | Fluent Bit | Workload cluster |
| Monitoring | Grafana Prometheus | Workload cluster |
User-managed packages can be installed via CLI by invoking the tanzu package install command. Before installing the user-managed packages, ensure that you have switched to the context of the cluster where you want to install the packages.
Also, ensure that the tanzu-standard repository is configured on the cluster where you want to install the packages.
You can run the command tanzu package repository list -A to verify this. Also, ensure that the repository status is Reconcile succeeded.
# Add Private Registry to the workload Cluster
tanzu package repository add tanzu-standard --url harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/tkgm-images/packages/standard/repo -n tkg-system
# tanzu package repository list -A
NAMESPACE NAME SOURCE STATUS
tkg-system tanzu-standard (imgpkg) harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/tkgm-images/packages/standard/repo Reconcile succeeded
#tanzu package available list -A
NAMESPACE NAME DISPLAY-NAME
tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com cert-manager
tkg-system contour.tanzu.vmware.com contour
tkg-system external-csi-snapshot-webhook.tanzu.vmware.com external-csi-snapshot-webhook
tkg-system external-dns.tanzu.vmware.com external-dns
tkg-system fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com fluent-bit
tkg-system fluxcd-helm-controller.tanzu.vmware.com Flux Helm Controller
tkg-system fluxcd-kustomize-controller.tanzu.vmware.com Flux Kustomize Controller
tkg-system fluxcd-source-controller.tanzu.vmware.com Flux Source Controller
tkg-system grafana.tanzu.vmware.com grafana
tkg-system harbor.tanzu.vmware.com harbor
tkg-system multus-cni.tanzu.vmware.com multus-cni
tkg-system prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com prometheus
tkg-system whereabouts.tanzu.vmware.com whereabouts
Install Cert Manager
The first package that you should install on your cluster is the cert-manager package which adds certificates and certificate issuers as resource types in Kubernetes clusters, and simplifies the process of obtaining, renewing and using those certificates.
-
Capture the available Cert Manager package versions.
NAMESPACE NAME VERSION RELEASED-AT tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.1.0+vmware.1-tkg.2 2020-11-24 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.1.0+vmware.2-tkg.1 2020-11-24 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.11.1+vmware.1-tkg.1 2023-01-11 12:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.5.3+vmware.2-tkg.1 2021-08-23 17:22:51 +0000 UTC tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.5.3+vmware.4-tkg.1 2021-08-23 17:22:51 +0000 UTC tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.5.3+vmware.7-tkg.1 2021-08-23 17:22:51 +0000 UTC tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.5.3+vmware.7-tkg.3 2021-08-23 17:22:51 +0000 UTC tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.7.2+vmware.1-tkg.1 2021-10-29 12:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.7.2+vmware.3-tkg.1 2021-10-29 12:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.7.2+vmware.3-tkg.3 2021-10-29 12:00:00 +0000 UT -
Install the
cert-managerpackage.Capture the latest version from the previous command. If there are multiple versions available, you must check the “RELEASED-AT” to collect the version of the latest one. This document uses the version 1.7.2+vmware.3-tkg.3 for installation.
The following command installs the
cert-managerpackage:tanzu package install cert-manager --package cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com --namespace cert-manager-package --version <AVAILABLE-PACKAGE-VERSION> # tanzu package install cert-manager --package cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com --namespace cert-manager-package --version 1.7.2+vmware.3-tkg.3 8:05:31AM: Creating service account 'cert-manager-cert-manager-package-sa' 8:05:31AM: Creating cluster admin role 'cert-manager-cert-manager-package-cluster-role' 8:05:31AM: Creating cluster role binding 'cert-manager-cert-manager-package-cluster-rolebinding' 8:05:31AM: Creating overlay secrets 8:05:31AM: Creating package install resource 8:05:31AM: Waiting for PackageInstall reconciliation for 'cert-manager' 8:05:31AM: Fetch started (1s ago) 8:05:32AM: Fetching | apiVersion: vendir.k14s.io/v1alpha1 | directories: | - contents: | - imgpkgBundle: | image: harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/tkgm-images/packages/standard/repo@sha256:cac4e2d8a3e98be121a86e687b57d8058dba5f0ba240f3db5008bc85e5ac04cf | path: . | path: "0" | kind: LockConfig | 8:05:32AM: Fetch succeeded 8:05:33AM: Template succeeded (1s ago) -
Confirm that the
cert-managerpackage has been installed successfully, and the status isReconcile succeeded.]# tanzu package installed get cert-manager -n cert-manager-package NAME: cert-manager PACKAGE-NAME: cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com PACKAGE-VERSION: 1.7.2+vmware.3-tkg.3 STATUS: Reconcile succeeded CONDITIONS: [{ReconcileSucceeded True }] USEFUL-ERROR-MESSAGE:
Install Contour
Contour is an open-source Kubernetes ingress controller providing the control plane for the Envoy edge and service proxy. Tanzu Kubernetes Grid includes signed binaries for Contour and Envoy, which you can deploy into workload clusters to provide ingress control services in those clusters.
After you have set up the cluster, you must first create the configuration file that is used when you install the Contour package and then install the package.
Package installation can be customized by entering the user-configurable values in YAML format. Following is an example YAML for customizing Contour installation:
---
infrastructure_provider: vsphere
namespace: tanzu-system-ingress
contour:
configFileContents: {}
useProxyProtocol: false
replicas: 2
pspNames: "vmware-system-restricted"
logLevel: info
envoy:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
annotations: {}
nodePorts:
http: null
https: null
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
disableWait: false
hostPorts:
enable: true
http: 80
https: 443
hostNetwork: false
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 300
logLevel: info
pspNames: null
certificates:
duration: 8760h
renewBefore: 360h
For a full list of user-configurable values, see Configure the Contour Extension.
-
Capture the available Contour package versions.
# tanzu package available list contour.tanzu.vmware.com -A NAMESPACE NAME VERSION RELEASED-AT tkg-system contour.tanzu.vmware.com 1.24.4+vmware.1-tkg.1 2023-04-28 00:00:00 +0000 UTCCapture the latest version from the previous command. If there are multiple versions available, check the “RELEASED-AT” to collect the version of the latest one. This document makes use of version 1.24.4+vmware.1-tkg.1 for installation.
-
Install the Contour package.
tanzu package install contour --package contour.tanzu.vmware.com --version <AVAILABLE-PACKAGE-VERSION> --values-file <path to contour-data-values.yaml> --namespace tanzu-contour-ingress # kubectl create namespace tanzu-system-ingress # kubectl create namespace tanzu-contour-ingress # tanzu package install contour --package contour.tanzu.vmware.com --version 1.24.4+vmware.1-tkg.1 --values-file contour-data-values.yaml --namespace tanzu-contour-ingress 8:12:04AM: Creating service account 'contour-tanzu-contour-ingress-sa' 8:12:04AM: Creating cluster admin role 'contour-tanzu-contour-ingress-cluster-role' 8:12:04AM: Creating cluster role binding 'contour-tanzu-contour-ingress-cluster-rolebinding' 8:12:04AM: Creating secret 'contour-tanzu-contour-ingress-values' 8:12:04AM: Creating overlay secrets 8:12:04AM: Creating package install resource 8:12:04AM: Waiting for PackageInstall reconciliation for 'contour' 8:12:04AM: Fetch started (1s ago) 8:12:05AM: Fetching | apiVersion: vendir.k14s.io/v1alpha1 | directories: | - contents: | - imgpkgBundle: | image: harbor.sfo01.rainpole.vmw/tkgm-images/packages/standard/repo@sha256:20db584c146086a789ab29e3efd24a8b406054a945607322abd134f38c603013 | path: . | path: "0" | kind: LockConfig | 8:12:05AM: Fetch succeeded 8:12:06AM: Template succeeded -
Confirm that the Contour package has been installed and the status is
Reconcile succeeded.# tanzu package installed get contour --namespace tanzu-contour-ingress NAME: contour PACKAGE-NAME: contour.tanzu.vmware.com PACKAGE-VERSION: 1.24.4+vmware.1-tkg.1 STATUS: Reconcile succeeded CONDITIONS: [{ReconcileSucceeded True }] USEFUL-ERROR-MESSAGE:
Install Harbor
Harbor is an open-source container registry. Harbor Registry may be used as a private registry for container images that you want to deploy to Tanzu Kubernetes clusters.
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid includes signed binaries for Harbor, which you can deploy into:
- A workload cluster to provide container registry services for that clusters.
- A shared services cluster to provide container registry services for other Tanzu Kubernetes (workload) clusters.
When deployed as a shared service, Harbor is available to all of the workload clusters in a given Tanzu Kubernetes Grid instance.
Follow this procedure to deploy Harbor into a workload cluster or a shared services cluster.
-
Confirm that the Harbor package is available in the cluster and retrieve the version of the available package.
# tanzu package available list harbor.tanzu.vmware.com -A NAMESPACE NAME VERSION RELEASED-AT tkg-system harbor.tanzu.vmware.com 2.8.2+vmware.2-tkg.1 2023-06-08 10:18:00 +0000 UTC -
Create a configuration file named
harbor-data-values.yamlby executing the following commands:image_url=$(kubectl -n tkg-system get packages harbor.tanzu.vmware.com.2.8.2+vmware.2-tkg.1 -o jsonpath='{.spec.template.spec.fetch[0].imgpkgBundle.image}') imgpkg pull -b $image_url -o /tmp/harbor-package --registry-ca-cert-path /etc/docker/certs.d/harbor.tanzu.lab/ca.crt cp /tmp/harbor-package/config/values.yaml harbor-data-values.yaml -
Set the mandatory passwords and secrets in the
harbor-data-values.yamlfile.bash /tmp/harbor-package/config/scripts/generate-passwords.sh harbor-data-values.yaml -
Edit the
harbor-data-values.yamlfile and configure the values for the following mandatory parameters:- namespace
- port
- harborAdminPassword
- secretKey
You can also change the values for other parameters to meet the requirements for your deployment. For the full list of the user-configurable values, see [https://techdocs.broadcom.com/us/en/vmware-tanzu/cli/tanzu-packages/latest/tnz-packages/packages-harbor-mc.html#deploy).
-
Remove the comments in the
harbor-data-values.yamlfile.yq -i eval '... comments=""' harbor-data-values.yaml -
Install the Harbor package by executing the following command:
# kubectl create namespace tanzu-system-registry # kubectl create namespace tanzu-harbor-registry # tanzu package install harbor --package-name harbor.tanzu.vmware.com --version 2.8.2+vmware.2-tkg.1 --values-file harbor-data-values.yaml --namespace tanzu-harbor-registry 8:01:14AM: Creating service account 'harbor-tanzu-system-registry-sa' 8:01:14AM: Creating cluster admin role 'harbor-tanzu-system-registry-cluster-role' 8:01:15AM: Creating cluster role binding 'harbor-tanzu-system-registry-cluster-rolebinding' 8:01:15AM: Creating secret 'harbor-tanzu-system-registry-values' 8:01:15AM: Creating overlay secrets 8:01:15AM: Creating package install resource 8:01:15AM: Waiting for PackageInstall reconciliation for 'harbor' 8:01:15AM: Fetch started (6s ago) | 8:04:50AM: L ongoing: waiting on pod/harbor-registry-78c99df744-v8psj (v1) namespace: tanzu-system-registry | 8:04:50AM: ^ Condition Ready is not True (False) | 8:04:52AM: ok: reconcile deployment/harbor-registry (apps/v1) namespace: tanzu-system-registry | 8:04:52AM: ---- applying complete [50/50 done] ---- | 8:04:52AM: ---- waiting complete [50/50 done] ---- | Succeeded 8:04:52AM: Deploy succeeded -
Confirm that the Harbor package has been installed and the status is
Reconcile succeeded.# tanzu package installed get harbor --namespace tanzu-system-registry NAME: harbor PACKAGE-NAME: harbor.tanzu.vmware.com PACKAGE-VERSION: 2.8.2+vmware.2-tkg.1 STATUS: Reconcile succeeded CONDITIONS: [{ReconcileSucceeded True }] USEFUL-ERROR-MESSAGE:
Install Prometheus
Prometheus is a system and service monitoring system. It collects metrics from configured targets at given intervals, evaluates rule expressions, displays the results, and can trigger alerts if some condition is observed to be true. The Alertmanager handles alerts generated by Prometheus and routes them to their receiving endpoints.
Do the following to deploy Prometheus into a workload cluster:
-
Capture the available Prometheus version.
# tanzu package available list prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com -A NAMESPACE NAME VERSION RELEASED-AT tkg-system prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com 2.27.0+vmware.1-tkg.1 2021-05-12 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com 2.27.0+vmware.2-tkg.1 2021-05-12 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com 2.36.2+vmware.1-tkg.1 2022-06-23 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com 2.37.0+vmware.1-tkg.1 2022-10-25 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com 2.37.0+vmware.2-tkg.1 2022-10-25 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com 2.37.0+vmware.3-tkg.1 2022-10-25 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com 2.43.0+vmware.2-tkg.1 2023-03-21 18:00:00 +0000 UTCCapture the latest version from the previous command. If there are multiple versions available check the “RELEASED-AT” to collect the version of the latest one. This document makes use of version 2.43.0+vmware.2-tkg.1 for installation.
-
Retrieve the template of the Prometheus package’s default configuration:
image_url=$(kubectl -n tkg-system get packages prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com.2.43.0+vmware.2-tkg.1 -o jsonpath='{.spec.template.spec.fetch[0].imgpkgBundle.image}') imgpkg pull -b $image_url -o /tmp/prometheus-package-2.43.0+vmware.2-tkg.1 --registry-ca-cert-path /etc/docker/certs.d/harbor.tanzu.lab/ca.crt cp /tmp/prometheus-package-2.43.0+vmware.2-tkg.1/config/values.yaml prometheus-data-values.yamlThis creates a configuration file named
prometheus-data-values.yamlthat you can modify. -
To customize the Prometheus installation, modify the following values:
Key Default Value Modified value Ingress.tlsCertificate.tls.crt Null Note: This is optional.
ingress.tlsCertificate.tls.key Null <Cert Key provided in Input file
Note: This is optional.
ingress.enabled false true ingress.virtual_host_fqdn prometheus.system.tanzu prometheus.your-domain To see a full list of user configurable configuration parameters, see Prometheus Package Configuration Parameters.
-
After you make any changes needed to the
prometheus-data-values.yamlfile, remove all comments in the file:yq -i eval '... comments=""' prometheus-data-values.yaml -
Install Prometheus package.
# kubectl create namespace tanzu-system-monitoring # kubectl create namespace tanzu-prometheus-monitoring # tanzu package install prometheus --package-name prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com --version 2.43.0+vmware.2-tkg.1 --values-file prometheus-data-values.yaml --namespace tanzu-prometheus-monitoring 8:20:09AM: Creating service account 'prometheus-tanzu-system-monitoring-sa' 8:20:09AM: Creating cluster admin role 'prometheus-tanzu-system-monitoring-cluster-role' 8:20:09AM: Creating cluster role binding 'prometheus-tanzu-system-monitoring-cluster-rolebinding' 8:20:09AM: Creating secret 'prometheus-tanzu-system-monitoring-values' 8:20:09AM: Creating overlay secrets 8:20:09AM: Creating package install resource 8:20:09AM: Waiting for PackageInstall reconciliation for 'prometheus' | 8:22:02AM: L ok: waiting on replicaset/alertmanager-56f6ccfc64 (apps/v1) namespace: tanzu-system-monitoring | 8:22:02AM: L ok: waiting on pod/alertmanager-56f6ccfc64-h5tl9 (v1) namespace: tanzu-system-monitoring | 8:22:03AM: ok: reconcile deployment/alertmanager (apps/v1) namespace: tanzu-system-monitoring | 8:22:03AM: ---- waiting on 1 changes [35/36 done] ---- | 8:22:23AM: ok: reconcile deployment/prometheus-server (apps/v1) namespace: tanzu-system-monitoring | 8:22:23AM: ---- applying complete [36/36 done] ---- | 8:22:23AM: ---- waiting complete [36/36 done] ---- | Succeeded 8:22:23AM: Deploy succeeded (1s ago) -
Confirm that the Prometheus package has been installed successfully and the status is
Reconcile succeeded.# tanzu package installed get prometheus -n tanzu-prometheus-monitoring NAME: prometheus PACKAGE-NAME: prometheus.tanzu.vmware.com PACKAGE-VERSION: 2.43.0+vmware.2-tkg.1 STATUS: Reconcile succeeded CONDITIONS: [{ReconcileSucceeded True }] USEFUL-ERROR-MESSAGE:
Install Grafana
Grafana allows you to query, visualize, alert on, and explore metrics no matter where they are stored. Grafana provides tools to form graphs and visualizations from application data.
Grafana is configured with Prometheus as a default data source. If you have customized the Prometheus deployment namespace and it is not deployed in the default namespace,
tanzu-system-monitoring, you need to change the Grafana data source configuration in the following code.
-
Retrieve the version of the available package.
# tanzu package available list grafana.tanzu.vmware.com -A NAMESPACE NAME VERSION RELEASED-AT tkg-system grafana.tanzu.vmware.com 7.5.16+vmware.1-tkg.1 2022-05-19 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system grafana.tanzu.vmware.com 7.5.17+vmware.1-tkg.2 2022-05-19 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system grafana.tanzu.vmware.com 7.5.7+vmware.1-tkg.1 2021-05-19 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system grafana.tanzu.vmware.com 7.5.7+vmware.2-tkg.1 2021-05-19 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system grafana.tanzu.vmware.com 9.5.1+vmware.2-tkg.1 2022-05-19 18:00:00 +0000 UTCCapture the latest version from the previous command. If there are multiple versions available check the “RELEASED-AT” to collect the version of the latest one. This document uses the version 9.5.1+vmware.2-tkg.1 for installation.
-
Retrieve the template of the Grafana package’s default configuration.
image_url=$(kubectl -n tkg-system get packages grafana.tanzu.vmware.com.9.5.1+vmware.2-tkg.1 -o jsonpath='{.spec.template.spec.fetch[0].imgpkgBundle.image}') imgpkg pull -b $image_url -o /tmp/grafana-package-9.5.1+vmware.2-tkg.1 --registry-ca-cert-path /etc/docker/certs.d/harbor.tanzu.lab/ca.crt cp /tmp/grafana-package-9.5.1+vmware.2-tkg.1/config/values.yaml grafana-data-values.yamlThis creates a configuration file named
grafana-data-values.yamlthat you can modify. For a full list of user-configurable values, see Grafana Package Configuration Parameters. -
Edit grafana-data-values.yaml and replace the following with your custom values.
Key Default Value Modified value secret.admin_password Null Your password in Base64 encoded format. grafana.service.type LoadBalancer NodePort ingress.virtual_host_fqdn grafana.system.tanzu User-Provided FQDN from Input File ingress.tlsCertificate.tls.crt Null Full chain cert provided in Input file ingress.tlsCertificate.tls.key Null Full chain cert provided in Input file -
(Optional) Modify the Grafana data source configuration.
Grafana is configured with Prometheus as a default data source. If you have customized the Prometheus deployment namespace and it is not deployed in the default namespace,
tanzu-system-monitoring, you need to change the Grafana data source configuration ingrafana-data-values.yaml.datasources: - name: Prometheus type: prometheus url: prometheus-server.<change-to-prometheus-namespace>.svc.cluster.local -
Remove all comments from
grafana-data-values.yamlfile.yq -i eval '... comments=""' grafana-data-values.yaml -
Install Grafana.
# kubectl create namespace tanzu-system-dashboards # kubectl create namespace tanzu-grafana-dashboards # tanzu package install grafana --package-name grafana.tanzu.vmware.com --version 9.5.1+vmware.2-tkg.1 --values-file grafana-data-values.yaml --namespace tanzu-grafana-dashboards 8:12:41AM: Creating service account 'grafana-tanzu-system-dashboards-sa' 8:12:42AM: Creating cluster admin role 'grafana-tanzu-system-dashboards-cluster-role' 8:12:42AM: Creating cluster role binding 'grafana-tanzu-system-dashboards-cluster-rolebinding' 8:12:42AM: Creating secret 'grafana-tanzu-system-dashboards-values' 8:12:42AM: Creating overlay secrets 8:12:42AM: Creating package install resource 8:12:42AM: Waiting for PackageInstall reconciliation for 'grafana' | 8:14:19AM: ongoing: reconcile deployment/grafana (apps/v1) namespace: tanzu-system-dashboards | 8:14:19AM: ^ Waiting for 1 unavailable replicas | 8:14:19AM: L ok: waiting on replicaset/grafana-58656c5f9b (apps/v1) namespace: tanzu-system-dashboards | 8:14:19AM: L ongoing: waiting on pod/grafana-58656c5f9b-mjphv (v1) namespace: tanzu-system-dashboards | 8:14:19AM: ^ Condition Ready is not True (False) | 8:14:31AM: ok: reconcile deployment/grafana (apps/v1) namespace: tanzu-system-dashboards | 8:14:31AM: ---- applying complete [18/18 done] ---- | 8:14:31AM: ---- waiting complete [18/18 done] ---- | Succeeded 8:14:31AM: Deploy succeeded -
Confirm that the Grafana package has been installed and the status is
Reconcile succeeded.# tanzu package installed get grafana -n tanzu-grafana-dashboards NAME: grafana PACKAGE-NAME: grafana.tanzu.vmware.com PACKAGE-VERSION: 9.5.1+vmware.2-tkg.1 STATUS: Reconcile succeeded CONDITIONS: [{ReconcileSucceeded True }] USEFUL-ERROR-MESSAGE:
Install Fluent Bit
Fluent Bit is a lightweight log processor and forwarder that allows you to collect data and logs from different sources, unify them, and send them to multiple destinations.
The current release of Fluent Bit allows you to gather logs from management clusters or Tanzu Kubernetes clusters running in vSphere, Amazon EC2, and Azure. You can then forward them to a log storage provider such as Elastic Search, Kafka, Splunk, or an HTTP endpoint.
The example shown in this document uses HTTP endpoint vRealize Log Insight for forwarding logs from Tanzu Kubernetes clusters.
-
Retrieve the version of the available package.
# tanzu package available list fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com -A NAMESPACE NAME VERSION RELEASED-AT tkg-system fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com 1.7.5+vmware.1-tkg.1 2021-05-13 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com 1.7.5+vmware.2-tkg.1 2021-05-13 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com 1.8.15+vmware.1-tkg.1 2022-05-24 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com 1.9.5+vmware.1-tkg.2 2022-06-23 18:00:00 +0000 UTC tkg-system fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com 2.1.2+vmware.1-tkg.1 2022-06-23 18:00:00 +0000 UTCCapture the latest version from the previous command. If there are multiple versions available, check the “RELEASED-AT” to collect the version of the latest one. This document uses the version 2.1.2+vmware.1-tkg.1 for installation.
-
Retrieve the template of the Fluent Bit package’s default configuration.
image_url=$(kubectl -n tkg-system get packages fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com.2.1.2+vmware.1-tkg.1 -o jsonpath='{.spec.template.spec.fetch[0].imgpkgBundle.image}') imgpkg pull -b $image_url -o /tmp/fluent-bit-2.1.2+vmware.1-tkg.1 --registry-ca-cert-path /etc/docker/certs.d/harbor.tanzu.lab/ca.crt cp /tmp/fluent-bit-2.1.2+vmware.1-tkg.1/config/values.yaml fluentbit-data-values.yaml -
Modify the resulting
fluentbit-data-values.yamlfile and configure the endpoint as per your choice. A sample endpoint configuration for sending logs to vRealize Log Insight Cloud over HTTP is shown in the following example.[OUTPUT] Name syslog Match * Host vrli.lab.vmw Port 514 Mode udp Syslog_Format rfc5424 Syslog_Hostname_key tkg_cluster Syslog_Appname_key pod_name Syslog_Procid_key container_name Syslog_Message_key message Syslog_SD_key k8s Syslog_SD_key labels Syslog_SD_key annotations Syslog_SD_key tkg -
Deploy Fluent Bit.
# kubectl create namespace tanzu-system-logging # kubectl create namespace tanzu-fluent-bit-logging tanzu package install fluent-bit --package-name fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com --version 2.1.2+vmware.1-tkg.1 --namespace tanzu-fluent-bit-logging --values-file fluent-bit-data-values.yaml ℹ Installing package 'fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com' ℹ Getting package metadata for 'fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com' ℹ Creating service account 'fluent-bit-tanzu-fluent-bit-logging-sa' ℹ Creating cluster admin role 'fluent-bit-tanzu-fluent-bit-logging-cluster-role' ℹ Creating cluster role binding 'fluent-bit-tanzu-fluent-bit-logging-cluster-rolebinding' ℹ Creating package resource ℹ Waiting for 'PackageInstall' reconciliation for 'fluent-bit' ℹ 'PackageInstall' resource install status: Reconciling ℹ 'PackageInstall' resource install status: ReconcileSucceeded ℹ Added installed package 'fluent-bit' -
Confirm that the Fluent Bit package has been installed and the status is
Reconcile succeeded.# tanzu package installed get fluent-bit --namespace tanzu-fluent-bit-logging NAME: fluent-bit PACKAGE-NAME: fluent-bit.tanzu.vmware.com PACKAGE-VERSION: 2.1.2+vmware.1-tkg.1 STATUS: Reconcile succeeded CONDITIONS: [{ReconcileSucceeded True }] USEFUL-ERROR-MESSAGE:
Appendix
Appendix A - Management Cluster Configuration File
AVI_CA_DATA_B64: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUVJVENDQXdtZ0F3SUJBZ0lVZVUrTTMvUHNlN2hkS3kwWG5WMGxFTk5jdHRBd0RRWUpLb1pJaHZjTkFRRUwKQlFBd2dhd3hDekFKQmdOVkJBWVRBbFZUTVFzd0NRWURWUVFJREFKRFFURVNNQkFHQTFVRUJ3d0pVR0ZzYnlCQgpiSFJ2TVE4d0RRWURWUVFLREFaV1RYZGhjbVV4R3pBWkJnTlZCQXNNRWxaTmQyRnlaU0JGYm1kcGJtVmxjbWx1Clp6RXNNQ29HQTFVRUF3d2pjMlp2TURGaGJHSmpkR3h5TURFdWMyWnZNREV1Y21GcGJuQnZiR1V1Ykc5allXd3gKSURBZUJna3Foa2lHOXcwQkNRRVdFV1Z0WVdsc1FHVjRZVzF3YkdVdVkyOXRNQjRYRFRJek1ETXhOakEyTkRVeApORm9YRFRJME1ETXhOVEEyTkRVeE5Gb3dnYXd4Q3pBSkJnTlZCQVlUQWxWVE1Rc3dDUVlEVlFRSURBSkRRVEVTCk1CQUdBMVVFQnd3SlVHRnNieUJCYkhSdk1ROHdEUVlEVlFRS0RBWldUWGRoY21VeEd6QVpCZ05WQkFzTUVsWk4KZDJGeVpTQkZibWRwYm1WbGNtbHVaekVzTUNvR0ExVUVBd3dqYzJadk1ERmhiR0pqZEd4eU1ERXVjMlp2TURFdQpjbUZwYm5CdmJHVXViRzlqWVd3eElEQWVCZ2txaGtpRzl3MEJDUUVXRVdWdFlXbHNRR1Y0WVcxd2JHVXVZMjl0Ck1JSUJJakFOQmdrcWhraUc5dzBCQVFFRkFBT0NBUThBTUlJQkNnS0NBUUVBcU1ZbmoyMWRETklveVdyMlJSYkEKdzhjei9DM0tTMU5WcXozTXJsWktNckQvUHhnVVJvc3c4Rzl5UkZ0aEZIRUJERXZYODhKY1gyYUtiRHFpaXRKVApiL2UvUHNuTkl4UlMvUG94T3UwQTFTMGJRZ3d1ZUpOMjNXc1NTeUJUR0RmeE1MT3p3NitONXFmZkdlY3Y1c2hlCmVRQjljaXZvTTJOZTJZVTFDVkFkcll5WFNJbWljdmFPZ2kvUlE1ZGpYY0VEMDg5TGRnQkV6TTgvckxCM1g0ZWQKMG05Qm10c1NQYUFja3JLZnRBZFBxMUlodHpFSGZaeno0VkF6VXFjdjkyQlR1eUM1cDVwUTRpSVZlSTlHZGxTQQoxL0kxNHQ5NTQ0M29saGVYWUY4bHR2Q2FkOGtsTFRIY1V0VjN2U0pUUm9hdFh2SzdMSmt3cmVZeTFKclQ5WTU1ClJ3SURBUUFCb3prd056QTFCZ05WSFJFRUxqQXNnaVJ6Wm04d01XRnNZbU4wYkhJd01XRXVjMlp2TURFdWNtRnAKYm5CdmJHVXViRzlqWVd5SEJLd1FDaEl3RFFZSktvWklodmNOQVFFTEJRQURnZ0VCQUJZV0xZdzZqaHFzU1pDVQp0WnBDYXB1OGl3RU9Ma3J0Q3N1WUkvd0dWUGtJRnIramJiRTFzMFkvTlBRb1VsalJwbDNRSFp4bzYveFFCQllMCnI4RHFxMk1UOHI0U0t1TXNmRGl6cTB6RHJUSUhwUjQ1RlBWV0dXRU05Q2hqeWJMRGJWazhyY1ZYZ2F4L3JIZUYKZlJGZmZka1lTdzRYNlpCbitYMmlYL1p0eHZxSStDbzFrdFNGZG9DSm5kbVRwdFAxaks3S3E4dGZiM05EYk9QaAp0dlRpY0s4SDRJY01SK2JwQUNKdTFxdHI3eThyTHZpa1l3S0dTLzR5WGh0Ky8zU3QxZVdFRWljYnpyTk1VN0FBCkhkZVNhYzlTc0Y1TDBsVkVnbVpNZUFKT1NrOE9tTVFzUnB5M29pRjMwQXZ5SDZqa0Jhc2QwcUNJUVlySjluUVQKMGoweU9Pbz0KLS0tLS1FTkQgQ0VSVElGSUNBVEUtLS0tLQ==
AVI_CLOUD_NAME: sfo01w01vc01
AVI_CONTROL_PLANE_HA_PROVIDER: "true"
AVI_CONTROL_PLANE_NETWORK: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip
AVI_CONTROL_PLANE_NETWORK_CIDR: 172.16.80.0/24
AVI_CONTROLLER: sfo01albctlr01.sfo01.rainpole.local
AVI_DATA_NETWORK: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkloadvip
AVI_DATA_NETWORK_CIDR: 172.16.70.0/24
AVI_NSXT_T1LR: /infra/tier-1s/sfo01w01tier1
AVI_ENABLE: "true"
AVI_LABELS: |
'type': 'management'
AVI_MANAGEMENT_CLUSTER_CONTROL_PLANE_VIP_NETWORK_CIDR: 172.16.80.0/24
AVI_MANAGEMENT_CLUSTER_CONTROL_PLANE_VIP_NETWORK_NAME: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip
AVI_MANAGEMENT_CLUSTER_SERVICE_ENGINE_GROUP: sfo01m01segroup01
AVI_MANAGEMENT_CLUSTER_VIP_NETWORK_CIDR: 172.16.80.0/24
AVI_MANAGEMENT_CLUSTER_VIP_NETWORK_NAME: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip
AVI_PASSWORD: <encoded:Vk13YXJlMSE=>
AVI_SERVICE_ENGINE_GROUP: sfo01w01segroup01
AVI_USERNAME: admin
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY: "harbor.tanzu.lab/tanzu-170"
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY: false
TKG_CUSTOM_IMAGE_REPOSITORY_CA_CERTIFICATE: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUZzVENDQTVtZ0F3SUJBZ0lKQUtvLzY4U3RGSC8vTUEwR0NTcUdTSWIzRFFFQkRRVUFNRzh4Q3pBSkJnTlYKQkFZVEFrTk9NUkl3RUFZRFZRUUlEQWxMWVhKdVlYUmhhMkV4RWpBUUJnTlZCQWNNQ1VKaGJtZGhiRzl5WlRFUApNQTBHQTFVRUNnd0dWazEzWVhKbE1Rd3dDZ1lEVlFRTERBTldUVU14R1RBWEJnTlZCQU1NRUdoaGNtSnZjaTUwCllXNTZkUzVzWVdJd0hoY05Nak13TXpJd01UUTBOakV5V2hjTk16TXdNekUzTVRRME5qRXlXakJ2TVFzd0NRWUQKVlFRR0V3SkRUakVTTUJBR0ExVUVDQXdKUzJGeWJtRjBZV3RoTVJJd0VBWURWUVFIREFsQ1lXNW5ZV3h2Y21VeApEekFOQmdOVkJBb01CbFpOZDJGeVpURU1NQW9HQTFVRUN3d0RWazFETVJrd0Z3WURWUVFEREJCb1lYSmliM0l1CmRHRnVlblV1YkdGaU1JSUNJakFOQmdrcWhraUc5dzBCQVFFRkFBT0NBZzhBTUlJQ0NnS0NBZ0VBMSs1NEJXNU0Kb0xIZ3BJRUZEUk9OTngyR2FtVkxPdEh0MlNVSWhmcmtlWXJ0Nlc4dWNoM3B3WUVOS3BuSGtaWU85a09kcnpIagpETENmSzR6dDdxY0J4R2pZSEJPY3pablkxL0oxWTRLU1l3UHc2ZzU2YU82MThFMGY3RDc4T05udkVZVjcxQlZJCmd3SmFoa0g1bCtTM3dURlZYd00xNGMxMTVNYitmV1Bmb1RSSGdwVnM2N1IzR0pFMGlBWEJDbHJRS3JsbDdCQWkKRDIxdVZxcnA1anEvd2xHUHN6ZkdDRUF3N21Wc2Z5RWIwWm1vV21jdnExRER1T3hLQjlFdjcyaUloRURmeDhJUgo1OWVTVHFvbzg2Q0xEaWxPMnduRVZuaEVBQy8wL0hGYUdmeWhLQ09neE50RWtER1c3ei9KWHNNb2Q3N3BhdzN4CkpqNEFSQWkvZ2ZlYVlIMjlGZnBWTHF2VitNazJydTF0ZHdING5RUTlra21CYlh2NDNIL3krSVBySDZxMUpFNlAKeGV0Lzh6UGE5RHd6eWs1Y0NPbHU0SDRLOSs5eGVnN0lKRk5jQk8reE1XQ2VtaUhlVXZ3SlBBRUcyQmFUSVduQwpxNGNFNEY5ck1ybHFHeW9sZkhURzFCSTR1dDl3NWRVbFViUlJuM0x5SHpZcG9tc1BvZ3lIb29QbXBiWk9hbTY4CjV4N1NZdEFka2ZnYW1kV2VPYU9Qc09Ob1VXenA1UTZIT0lHaVI3Z2ZiU3Yxa3owNzBnYXMvRlJVK1F4ZkVkWncKeGhOWjlvUENBYWJFMVJPRkhhTGszNFUrZ2lHclNiZmNzUUdZcFBYZUR0TS9GSUlsTGdiSGMrZEZINWNUbmcwLworR2RUR01qdkI5UHJTc05VekJTMGdNK3dTT3luKzZqWXJtMENBd0VBQWFOUU1FNHdIUVlEVlIwT0JCWUVGTHl3CnErVENpRDZxNllvTy9IMnNmRnE1cE1ERE1COEdBMVVkSXdRWU1CYUFGTHl3cStUQ2lENnE2WW9PL0gyc2ZGcTUKcE1ERE1Bd0dBMVVkRXdRRk1BTUJBZjh3RFFZSktvWklodmNOQVFFTkJRQURnZ0lCQUJ4dkxQWUg4dTFudTZVMQpScEhMQ1JLVy91eGlBS3ZHR1UyWkR0ZVArS243Qml1RlorNlBWZE9EaVI0QjRqcmxCc241TkhvanBoa2tTL2QrCmJkRFB3NlRtb2RTWjFhcjdNQUNSODFRdlpLcmtSUm05VklZdVJwMTExalliRWowY1dHbUp6eVhZQWZxREMydFMKUCs4NWYzazlrT2ZpclFhWld3SkJGcDViSklLNmhKam5DN3NwdmJaRHRqTGgvZTBRbXdzNHRveWRGOTRMaEdrZAp2cXB4OWJuSXIrV1cyTkNKbzRGa3ppMnhJcDRnVG50N1Z2bkI0MnFLaW80a0FxbXpDN1VSU3daVWYrT1NKUkpFCm5RNWpLbEF0MllZZnE0b0F4OVN6dm5wWjRQSkhKT1FseEJTNmplWkh6UzRjdS9qMHIwbHRkdDh4MWo0eEkwQSsKK01oSXRpdVVlWEZMUHNJYjdFRU9zUjlZblUxOVdTd0lUYTAyMVFVVVVHTWlvRlhhYno0VkpEY2V1K0YvK1d2Rgp6RndXMDBvbTZ0dWREbm9qVFpzcEc4cUhkS2NiLytSRzJVak14amVMRCtrRmdsZGozc3hOZWwxdldhMWNnK0hzCkd5UFl5ejJlUlFyRG5yU21QMFN5QlFpallZV1QwNTd4TUUwK1M0ZzdZQXRKQWFPNDdtbW41dWRxQ2lmNmZlcHMKYW5Sd3hnOHY3N1Zvb2IvZUdxZFBjZmpNQXZEdm1Ed0VhZW1OWnJOM1g2ODlJdllTdkF2R1AwY2ovKzc1VVJBNApSOTFYU3FPdUMrd0RzRXVUUlNsQ1ZDMzhZNzJpQmNnK2VtUjg2dWc1M1Y4WVQyVTRwWVEwdkRMR3NZNWduWGlFCmVpSEFmK0M1TGhrMlc2ZnRBUElnRUdRV3NET0kKLS0tLS1FTkQgQ0VSVElGSUNBVEUtLS0tLQo=
CLUSTER_ANNOTATIONS: 'description:,location:'
CLUSTER_CIDR: 100.96.0.0/11
CLUSTER_NAME: sfo01w01tkgmgmt01
CLUSTER_PLAN: prod
ENABLE_AUDIT_LOGGING: "true"
ENABLE_CEIP_PARTICIPATION: "true"
ENABLE_MHC: "true"
IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPE: none
INFRASTRUCTURE_PROVIDER: vsphere
LDAP_BIND_DN: ""
LDAP_BIND_PASSWORD: ""
LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_BASE_DN: ""
LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_FILTER: ""
LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_GROUP_ATTRIBUTE: ""
LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_NAME_ATTRIBUTE: cn
LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_USER_ATTRIBUTE: DN
LDAP_HOST: ""
LDAP_ROOT_CA_DATA_B64: ""
LDAP_USER_SEARCH_BASE_DN: ""
LDAP_USER_SEARCH_FILTER: ""
LDAP_USER_SEARCH_NAME_ATTRIBUTE: ""
LDAP_USER_SEARCH_USERNAME: userPrincipalName
OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_CLIENT_ID: ""
OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_CLIENT_SECRET: ""
OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_GROUPS_CLAIM: ""
OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_ISSUER_URL: ""
OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_NAME: ""
OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_SCOPES: ""
OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_USERNAME_CLAIM: ""
OS_ARCH: amd64
OS_NAME: photon
OS_VERSION: "3"
SERVICE_CIDR: 100.64.0.0/13
TKG_HTTP_PROXY_ENABLED: "false"
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_CUSTOM_VMX_KEYS: ""
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_DISK_GIB: "40"
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_ENDPOINT: ""
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_HARDWARE_VERSION: ""
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_MEM_MIB: "8192"
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_NUM_CPUS: "2"
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_PCI_DEVICES: ""
VSPHERE_DATACENTER: /sfo01w01dc01
VSPHERE_DATASTORE: /sfo01w01dc01/datastore/vsanDatastore
VSPHERE_FOLDER: /sfo01w01dc01/vm/tkg-management-components
VSPHERE_IGNORE_PCI_DEVICES_ALLOW_LIST: ""
VSPHERE_INSECURE: "false"
VSPHERE_NETWORK: /sfo01w01dc01/network/sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgmanagement
VSPHERE_PASSWORD: <encoded:Vk13YXJlMSE=>
VSPHERE_RESOURCE_POOL: /sfo01w01dc01/host/sfo01w01cluster01/Resources/tkg-management-components
VSPHERE_SERVER: sfo01w01vc01.sfo01.rainpole.local
VSPHERE_SSH_AUTHORIZED_KEY: ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAACAQC0mAnVUaKqvQQilprtq5WMQL3Xf6MVxhKzxvZwqS6thXDD4ET2hqcmztAJorKBqwI6aX5mVM8cIy5lUmLYcsW6PaRt24+wY2JInqtPxr/06VIp2CZts+46d8PZ4fQCoqI59yPwE0AU8EOvS9k9AxUPIJwLMbsYMFgu2yveU5sTG0jgYuGodkghMul1ohfMh8WpKKSnq4QM6Pll0t2k1CfOviwmRDJECET/K34XgFigLx1CbI5HfyTeG84TFPBJs8OiWZMjCEG3++xW1nV9kpLP2JyOBmDCDVJNS2ZqlGXUkCWaaXQ/VJnPOJIEQHCoJ2GT2mUrjW4kUcrlHkmO04a1Fu3q7RmVxDLKAVxZOc1tkKHqhUKqbdRYc71vftpI8n9os/hxU4N0uKLuW4ymw2n3+LNiUWVU9UKVOZ3LUT+rm2JlIi/ooTwkwJM+48BeKQ1uC0jqIAcafpSk9PibXj1BR1Qp7PpB/97d3hUVYfNoiT3zDfyQbDfbwgVMr/DG4Bhow3n34iV72nRLdqPm81ckUUZEvbftX9ylYsqm2U4X1zTVAZDXAXUlylyV2bGdt5usoKtp5lK3xI+WlqTEP+WQ65WRBP+gJkjxoe1QkYjYJS8u3sysy8M/sxJLElutVvAzwBfitYYRAm49A2gTTuekDtELjmKIjgNGALikk1qB/Q== email@example.com
VSPHERE_TLS_THUMBPRINT: 7F:BA:25:AC:DD:B9:89:DD:04:EB:89:B8:76:74:18:F4:23:EC:75:17
VSPHERE_USERNAME: administrator@vsphere.local
VSPHERE_WORKER_CUSTOM_VMX_KEYS: ""
VSPHERE_WORKER_DISK_GIB: "40"
VSPHERE_WORKER_HARDWARE_VERSION: ""
VSPHERE_WORKER_MEM_MIB: "8192"
VSPHERE_WORKER_NUM_CPUS: "2"
VSPHERE_WORKER_PCI_DEVICES: ""
WORKER_ROLLOUT_STRATEGY: ""
Appendix B - Single VIP Nertwork Architecture - Shared Service Cluster ADC file
apiVersion: networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: AKODeploymentConfig
metadata:
generation: 3
name: tanzu-ako-for-shared
spec:
adminCredentialRef:
name: avi-controller-credentials
namespace: tkg-system-networking
certificateAuthorityRef:
name: avi-controller-ca
namespace: tkg-system-networking
cloudName: sfo01w01vc01
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
type: shared-services
controlPlaneNetwork:
cidr: 172.16.80.0/24
name: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip
controller: 172.16.10.10
controllerVersion: 22.1.3
dataNetwork:
cidr: 172.16.80.0/24
name: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip
extraConfigs:
disableStaticRouteSync: false
ingress:
defaultIngressController: false
disableIngressClass: true
nodeNetworkList:
- networkName: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgmanagement
networksConfig:
nsxtT1LR: /infra/tier-1s/sfo01w01tier1
serviceEngineGroup: sfo01m01segroup01
Appendix C - Single VIP Nertwork Architecture - Workload Cluster ADC file
apiVersion: networking.tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: AKODeploymentConfig
metadata:
generation: 3
name: install-ako-for-workload-02
spec:
adminCredentialRef:
name: avi-controller-credentials
namespace: tkg-system-networking
certificateAuthorityRef:
name: avi-controller-ca
namespace: tkg-system-networking
cloudName: sfo01w01vc01
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
type: workload-02
controlPlaneNetwork:
cidr: 172.16.80.0/24
name: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip
controller: 172.16.10.10
controllerVersion: 22.1.3
dataNetwork:
cidr: 172.16.80.0/24
name: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgclustervip
extraConfigs:
disableStaticRouteSync: true
ingress:
defaultIngressController: true
disableIngressClass: false
serviceType: NodePortLocal
shardVSSize: MEDIUM
nodeNetworkList:
- networkName: sfo01-w01-vds01-tkgworkload
cidrs:
- 172.16.60.0/24
networksConfig:
nsxtT1LR: /infra/tier-1s/sfo01w01tier1
serviceEngineGroup: sfo01w01segroup01
Content feedback and comments